The Sabre 28 was the smallest boat in the line produced by Sabre Yachts of South Casco, Maine for much of the company’s history. The production run of the 28 lasted 14 years, from 1972 to 1986.
The Sabre 28 was the only model produced by the company until 1977, when the Sabre 34 entered production. In 1979 the gap between the Sabre 28 and the 34 was filled with a 30-footer of a design very similar to that of her two sisters. In 1982, the Sabre 38 was introduced, and features both a standard and an aft-cabin layout. A 32 was added in 1984, a 36 in 1985, and a 42-footer in 1987. Along the way, the 28 acquired a ketch-rig option. The 28 was dropped at the same time the 42 was introduced.
All boats in the Sabre line are of the modern cruiser-racer type, with fin keel and skeg-hung spade rudder. With a 1981 base price of about $37,000, and an average delivered price in southern New England of about $40,000 without sails or electronics, the Sabre 28 was a relatively expensive 28′ boat.
Despite a fairly high initial cost, the Sabre 28 has proved to be a good investment for her owners. One owner responding to The Practical Sailor’s boatowners’ survey reported that he paid $14,900 for his boat in 1973. That same boat in 1981 was worth about $24,000. A Sabre 28 purchased in 1976 cost $22,000, and was worth about $29,000 in 1981. The collapse of market values in the ’90s is evident in the latest figures, however: a 1986 Sabre 28, which cost $48,900 new, is now worth only about $34,000. This is typical of recent trends, and does not reflect on the Sabre 28—indeed, it’s held more of its value than many boats.
Owners report that the primary motivation for purchasing the boat can be summed up in one word: quality. Sabre is quite conscious of their producing a high-quality boat. The boat attracts buyers willing to pay a little more than average for a boat that is better than average.
As with all boats that have been in production for a number of years, the design of the Sabre 28 has evolved and improved over the years. In particular, a number of minor changes were made in August, 1982, some of which are noted below. Therefore, the price of a used Sabre 28 may be a function of whether it has some of the more desirable features.
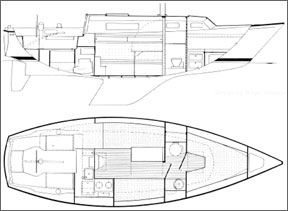
The Sabre 28 is conventionally modern in appearance. She has a modest concave sheer, straight raked stern, and short after overhang.
Construction
The hull of the Sabre 28 is a slightly heavier-than-average hand layup of mat and roving. Some roving print through is evident, but there are no visible hard spots in the hull. Gelcoat quality is excellent.
There are optional hull and deck colors besides the stock white on white. On an early Sabre 28 we examined, the red gelcoat had faded to a dull pink, and the boat was past due for painting. In general red hulls are more susceptible to fading.
The deck of the Sabre 28 is balsa-cored for stiffness, with plywood inserts at stress areas such as winch mountings. The hull-to-deck joint uses a fairly standard internal hull flange, butyl-bedded and through bolted on 6″ centers with stainless steel bolts. These bolts also serve to attach a vinyl rubrail and the teak toerail: The hull-to-deck joint is through bolted across the transom.
All deck hardware, including stanchions, pulpits, and cleats, is through bolted and backed with thick aluminum plates which serve to distribute load. The stem fitting is a well-finished aluminum casting.
Skin fittings are recessed flush with the hull surface. All underwater through hull openings are fitted with bronze Spartan seacocks. Spartan seacocks have a short, lipped hose tailpiece rather than the more typical long straight tailpiece of other seacocks.
This short tailpiece precludes double clamping of hoses. This single hose clamp on below-water fit tings is fine as long as the hose clamps are kept tight. We recommend that they be checked at regular intervals.
In general, construction details are among the best that we’ve seen on a production sailboat. All fillet bonding is absolutely neat. There are no rough fiberglass areas anywhere. All exposed interior fiberglass surfaces, such as bilges and the inside of lockers, are gelcoated or painted.
Although tiller steering is standard, about 90% of the boats were delivered with Edson pedestal wheel steerers equipped with Ritchie compasses. The wheel steering option has proven so popular that in 1976 the cockpit of the Sabre 28 was redesigned to accommodate the wheel without interfering with the seating arrangement. Access to the rudder stock for emergency steering is via a plastic plate in the cockpit sole. An emergency tiller is provided with wheel-steered boats.
The mast of the Sabre 25 is a straight section Awlgripped aluminum extrusion built by Rig-Rite. Internal halyards, internal clew outhaul, topping lift, and two-point jiffy reefing are standard, as is a transom-mounted ball-bearing mainsheet traveler. The mast is deck-stepped in an aluminum casting. In new boats, this mast step has been redesigned to incorporate attachment points for blocks, facilitating the leading of halyards aft to the cockpit. Halyard winches mounted on the cabin top are another popular option.
Mast compression is transferred to the hull structure by a teak compression column incorporated in the main bulkhead. Shroud chainplates are heavily through-bolted to the main bulkhead, which is solidly glassed to the hull.
Originally, the Sabre 28 was rigged with single upper and lower shrouds. In 1975 forward lower shrouds were added to reduce mast pumping under sail and vibration at the mooring. Mast vibration in high winds, even at anchor, is a common problem with deck-stepped masts. Not all older Sabre 28s have been retrofitted with the additional set of lower shrouds. If purchase of a pre-1975 model is contemplated, be sure to ascertain that the forward lower shrouds have been installed.

The ballast keel is an external lead casting, well faired to the hull. Keelboats are accessible in the bilge for periodic tightening.
Construction of the Sabre 28 is strong without being overly heavy. There is no evidence of hurrying to finish the job anywhere in the boat.
Handling Under Sail
With optional wheel steering, optional cockpit-led halyards, and optional self-tailing headsail sheet winches, the Sabre 28 can easily be handled by one or two people. The mainsheet is within easy reach of the helmsman. Unfortunately, his head is also within easy reach of the mainsheet when jibing, except on newer boats; the mainsheet was relocated to the cabin top in 1982.
With main chainplates set well inboard, the headsail sheeting base of the boat is quite narrow, particularly if the boat is equipped with the optional inboard genoa track in addition to the standard toerail-mounted genoa track, The sheeting base is, for example, almost a foot narrower than that of the Hunter 27. This allows the Sabre 28 to be reasonably close-winded. With her relatively small wetted surface and a big genoa, she will be fast in light air.
Unless the water in your cruising area is spread very thin, we suggest you look for the standard keel version rather than the shoal keel. The shoal keel presents a less efficient lateral plane for windward work.
Some attention will have to be paid to the size of headsail used. Owners report that, although the Sabre 28 more than holds her own with other boats of her size and type, she is not a particularly stiff boat. Owners consider her performance well above average, although her PHRF rating suggests only average performance compared to similar cruiserracers. Due to the off-center solid prop, the boat may be faster on one tack than the other, and owners who intend to race the Sabre 28 should experiment to see if this is the case.
Handling Under Power
Several different engines were used in the Sabre 28. Until 1975 all were equipped with the Atomic Four gasoline engine. In 1975 a 10 horsepower Volvo diesel was offered as an option. In 1978, both these engines were dropped, and the Volvo MD7A diesel became standard. The MD7A is a two cylinder engine rated at 13 horsepower. In 1981 it was replaced by the Westerbeke 13.
The propeller shaft on the right hand turning Atomic Four is offset to port. On the left hand turning Volvos, it is offset to starboard. On the earliest Sabre 28s the shaft was on centerline. This change in engines from right hand to left hand rotation means that replacement of engines in off-center located Atomic Four powered boats will be limited to either the Atomic Four gas engine or some other right hand turning engine. Otherwise there will be considerable compromise in handling characteristics under power.
Owners report that engine access on early Atomic Four equipped models is poor. In current Volvo-powered models, access for routine service is good. Some joinerwork disassembly—planned in, fortunately—is required for engine removal, Routine service is via doors and panels.
There is no oil sump under the engine. Access to the stuffing box, needed annually for repacking and adjustment, is poor. Engine instruments—a full bank, with no idiot lights —are mounted in the bridgedeck, with engine starting and stopping controls under the helmsman’s seat. While this may seem awkward at first, it does protect the always-vulnerable ignition switch from water. This is an unusual, but reasonable arrangement.
Owners consider the boat’s handling under power to be good. With her fin keel and spade rudder, she will turn in a tight circle. Owners report that any of the engines will drive the boat at or near “hull speed” under most conditions,
Deck Layout
In 1976, a foredeck anchor well was added to the Sabre 28. The well is large enough to hold adequate primary ground tackle for the boat. It has provision for securing the bitter end of the anchor rode in boats built since 1982. We would add an eyebolt or U-bolt to the well for this purpose if it is not already there.
The water tank vent is located in the anchor well. This is a rational location for an item whose position is commonly an afterthought. Frequently, tank vents are located in the topsides, just below the sheer, This can cause backsiphoning of salt water into fuel or freshwater tanks. We saw this occur on several boats—not Sabres—in the 1979 Marion-Bermuda race, which featured four days of slogging to windward in heavy air.
The Sabre 28 is one of the few boats we have seen that uses Skene bow chocks. Skene chocks effectively hold the anchor rode or mooring lines in the chocks, even if the boat sails around on her anchor. This is an important consideration in many modern boats, for the Sabre 28, like many modern sloops of moderate displacement, probably sails almost as many miles while anchored or moored as when underway.
Heavy teak handrails and a very effective molded-in nonskid surface facilitate movement on deck in a seaway. The side decks are of necessity narrow due to the wide cabin trunk.
The cockpit of the Sabre 28 is large and comfortable. It is as large a cockpit as we would consider safe for offshore sailing on a 28′ boat. With wheel steering the cockpit easily seats five.
Cockpit lockers deserve special comment. There are two molded-in recesses in the winch islands, handy for winch handles, sail stops, and other small items. There is a shallow lift-top locker under the port cockpit seat, a deeper locker under the helmsman’s seat, and a deep locker under the starboard seat.
The deep starboard locker is bulkheaded off from the bowels of the boat so that sails, fenders, and lines will not migrate to the depths of the bilge. This locker contains built-in holders for the companionway drop boards and emergency tiller, as well as a shelf arranged for line stowage. Although the lid to this locker is a little small for the easy removal of sails, it is one of the best designed cockpit lockers we have seen.
By comparison, the companionway is a bit of a disappointment. Although it is suitably narrow and has a good bridgedeck, the opening is sharply tapered, allowing removal of the drop boards by lifting them only about an inch.
The drop boards themselves are 1/2″ teak-faced plywood in early boats, solid teak in post-1982 models. The exposed edge grain of the plywood core will soon turn gray unless the boards are well varnished. Eventually they may delaminate. We believe that plywood should not be used where it will be subject to weathering. Frankly, the boards look a little cheap on a boat of this quality.
Newer boats have a transparent smoked plexiglass companionway hatch top. Older boats have fiberglass hatches. The plexiglass hatch allows a good deal of light below.
At night, when tied to the dock, it also allows people on the dock to stare into the main cabin. An often forgotten corollary to transparent hatches is that if they allow light below during the day, they allow it out at night. The glare of a white light belowdecks can wipe out the helmsman’s night vision. Not a common problem, admittedly, but a real one nonetheless.
Belowdecks
The first impression of the Sabre 28 belowdecks is that she is roomy, neat, and well-finished. Headroom is 6′ under the main hatch, and an honest 5′ 11″ in the main cabin.
The forward cabin contains V-berths with a filler to form a double. The 30-gallon molded polyethylene water tank is located under the forward berths. There is a drawer and a bin under each berth.
With the forward hatch open, it is possible to stand and dress comfortably with the berth filler removed.
The head is full width and closes off from both the forward cabin and main cabin by doors. The Sabre 28 came standard with a 22-gallon holding tank. A Y-valve diverter was optional.
Despite a lot of teak bulkheads and trim, the main cabin is bright and attractive. There are substantial grab rails overhead. The port settee extends to form a double berth. With all berths filled, the Sabre 28 sleeps six. Frankly, six people on a 28′ boat is too many, even for a weekend. We would prefer an alternate four-berth interior arrangement that provides a larger galley. Some older Sabre 28s are equipped with such a layout.
A bulkhead-mounted fold-down cabin table seats four comfortably. It is secured in the folded position by a screw-type hatch dog, a good idea, since a rattling table can drive you to distraction.
At the after end of the main cabin, the galley is located to starboard, with a quarterberth to port. Galley storage is good, with four drawers and several lockers. The galley sink is located just off centerline, almost under the companionway. While this location is good for ensuring that the sink will drain on either tack, care must be taken going below when well heeled on the port tack to avoid stepping into the sink.
The galley stove is a recessed two-burner Kenyon alcohol stove. Stoves of this type, which have integral fuel tanks with the fuel fill located between the burners, present a potential fire hazard if the fuel tank is refilled before the burners have cooled adequately.
On pre-1982 boats, the icebox is well insulated with the exception of the top. Given the fact that Sabre has gone so far as to install an icebox pump to keep ice melt from smelling up the bilge, we were pleased to see them complete the otherwise well designed icebox in 1982 by insulating the top and lids.
Wiring, plumbing—in general, all finishing details—are well designed and neatly finished. The location of the main electrical panel next to the companionway, where it is vulnerable to spray, is an exception to the generally well thought out installations.
Four opening ports are standard; an additional hatch over the main cabin is optional. We recommend this additional ventilation if the boat is to be used in a warm climate. The dorade box over the head is the only provision for foul-weather ventilation.
Conclusions
The Sabre 28 is an attractive, well-built, well-finished boat. Although her price is above average, construction and finish details are also well above average for a stock boat. Despite her modern underbody, she is a conservative design, conservatively built.
The Sabre 28 is neither an all-out racer, nor an allout cruiser. She is a good compromise boat, strong enough to cruise with confidence and fast enough not to embarrass.
She is good-looking in a modern way, without being so modern as to be trendy. She will probably not appeal to the hard-core traditionalist, nor to the flat-out modernist. She appeals mostly as a well turned out coastal cruiser for the couple or a small family. The Sabre 25 may be no Swan, but she’s a long way from an ugly duckling.



































Appreciate your in depth comments on this yacht. I raced aboard one on Long Island Sound in the mid 70’s. I echo your sentiments and conclusion.
Is the motor cruiser version safe to use in the offshore UK waters?