We receive many requests from readers to review certain boats. Almost without exception, the requests come from owners of the boat suggested. Few boats have been the object of more requests than the venerable Morgan 38. At first blush, it is difficult to determine which Morgan 38 we ought to address, as two distinct designs were built since the first one appeared 22 years ago. After some thought, we decided to trace the history of both as best we could, including also the Morgan 382, 383 and 384.

History
The Morgan 38 was designed in 1969 by Charlie Morgan. He had founded Morgan Yacht Company in St. Petersburg, Florida, in 1965. The Morgan 34 was his first production model. A hometown boy, he had made a name for himself in the 1960 and 1961 Southern Ocean Racing Conference (SORC), winning with a boat of his own design called Paper Tiger. While not a formally trained naval architect, Morgan demonstrated his skill with a variety of designs. Many of these were keel/centerboard models, owing to the shoalness of Florida waters. Seventy-nine were built before production halted in 1971.
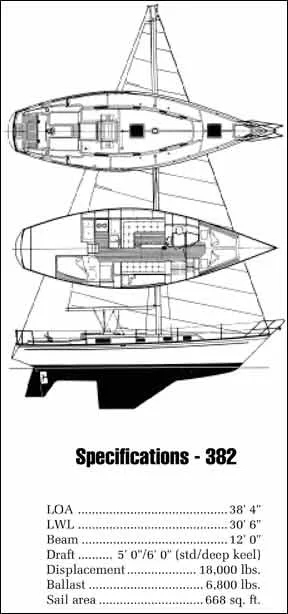
In 1977, the Morgan 382 was introduced, designed by Ted Brewer, Jack Corey and the Morgan Design Team. According to Brewer, the boat was loosely based on the Nelson/Marek-designed Morgan 36 IOR One Ton. The most obvious difference between the 38 and 382 was the elimination of the centerboard and the addition of a cruising fin keel (NACA 64 012 foil) with skeg-mounted rudder. They are two completely different designs from two different eras in yacht design.
In 1980, the 382 was given a taller rig and called the 383. About 1983 the boat underwent other subtle changes, now called the Morgan 384. The rudder was enlarged and the interior modified. In its three versions, the Brewer model registered about 500 sales.
The company changed ownership several times during this period. It went public in 1968, was later bought by Beatrice Foods and then Thor Industries. Presently it is owned by Catalina Yachts, who built just 24 38s (three were kits) before discontinuing production in 1986.
Design
The first Morgan 38 was a development of the highly successful 34, which Morgan called a “beamy, keelcenterboard, CCA (Cruising Club of America)-style of yacht. We had a good thing going and didn’t want to deviate; we found little interest in those days in keel boats. Centerboards have their own sorts of problems, but there’s an awful lot of thin water in the world, and safe refuge and quiet anchorages are mostly in shoal water.”
The boat has a long, shoal keel drawing just 3′ 9″ with the board up. The rudder is attached and there is an aperture for the propeller. “Beamy,” in 1969, meant 11 feet. The waterline was fairly short at 28 feet, but the overhangs give the hull a very balanced and pleasing profile. The stern is pure Charlie Morgan—a finely proportioned shape that is neither too big nor too small. In profile, the angle between the stern (which interestingly is a continuation of the line of the backstay) and the counter is nearly 90 degrees. It’s a trademark look.
Sloop and yawl rigs were offered, which was typical of CCA designs. The rig has a lower aspect ratio (the proportion of the hoist to the foot of the mainsail) than later designs, including the Brewer-designed 382. Yet this is a very wholesome rig for cruising. Owners responding to our questionnaire said the boat balances very well.
Owners of the 382 and subsequent permutations seemed less pleased. They didn’t rate balance as highly, noting most frequently the difficulty in tracking (keeping the boat on a straight course) when sailing off the wind (not uncommon with beamy fin keel designs; it’s a trade-off with speed, pointing ability and maneuverability). Others said that they raked their masts forward to improve balance. One thought the problem was caused because the rudder was slightly undersized. Still, these owners liked the way their boats sail.
The rig, of course, isn’t the only difference between the Morgan and Brewer designs. The latter has a foot wider beam—12 feet—and a longer waterline. Two keels were offered, the standard five-foot draft and an optional deep keel of six feet. Displacement jumped a thousand pounds to 17,000 despite a reduction in ballast from 7,500 pounds to 6,600 pounds. Centerboard boats, naturally, require more ballast because it isn’t placed as low as it is in a deep fin keel boat.
The look of the 382 is much more contemporary. The rake of the bow is straighter, as is the counter, which is shorter than the original 38 as well. Freeboard is higher and the windows in the main cabin are squared off for a crisper appearance.
Construction
The hulls of the early 38s were built of solid fiberglass and the decks of sandwich construction. Some 382 hulls were cored, others not. A variety of core materials were used, mostly Airex foam. The lamination schedule was your basic mat and woven roving, with Coremat added as a veil cloth to prevent printthrough.
Both designs have internal lead ballast, sealed on top with fiberglass.
The early 382s did not have the aft bulkhead in the head fiberglassed to the hull, which resulted in the mast pushing the keel down. All boats “work” under load, and bulkheads bonded to the hull are essential to a stiff structure. Anyone who has a boat in which major load-bearing bulkheads are not attached to the hull should do so before going offshore. To its credit, the company launched a major recall program.
The owners of all Morgan 38s, as a group, note the strength of the boat. One said he hit a rock at 6 ½ knots and suffered only minor damage. Very few problems were mentioned. The owner of a 1981 model, however, said he “drilled through hull at waterline and was surprised at thinness of glass on either side of the Airex: 1/8” inside, 1/16″ outside.” With the stiffness that sandwich construction provides, not as much glass is required; still, protection from collision and abrasion would recommend greater thickness outside. Brewer, incidentally, discounted the report.
Interestingly, Hetron-brand fire-retardant resin was used for a time, prior to 1984; if you recall, this was blamed for the many cases of reported blistering on the early Valiant 40s. About half of the 382 owners responding to our surveys reported some blistering, none serious.
The attached rudder of the early 38 is stronger than the skeg-mounted rudder of later models. But we do prefer the skeg configuration to a spade rudder, at least for cruising. A problem with skegs, however, is the difficulty in attaching them strongly to the hull. One owner said his was damaged in a collision with a humpback whale, but that is hardly normal usage!
Several owners of later models commented that the mast was a “utility pole,” recommending a custom tapered spar for those inclined to bear the expense.
Other problems reported in our survey were only minor and were corrected by the company. In fact, owners were nearly unanimous in their praise for Morgan Yachts’ customer service.
Interior
The layout of the Morgan 38 is quite conventional and workable. In both incarnations there are Vberths forward, private head with shower (separate enclosure in the 382), dinette in main cabin with settee, galley aft in the port quarter area and nav station with quarter berth opposite to starboard. Specifications for the first 38s included “attractive wood-grained mica bulkhead paneling, with oiled American walnut trim.” This was a popular treatment in the 1960s, and practical, but often done to excess. By the 1980s, fake teak didn’t play so well. Owners wanted real wood, and that’s what they got in the 382.
Owners of early 38s complained of poor ventilation (“I added six opening ports, and would like an additional center cabin hatch,” wrote one), short Vberths (“Could be 4″ longer, but I’m 6′ 2.””), and more closet space (from a live-aboard).
Owners of later models mentioned the need for a larger forward hatch to get sails through, a hatch over the galley, larger cockpit scuppers, and Dorade vents.
(Teak Dorade boxes were added on the 384.) They complained of not enough footroom in the V-berths and poor location of the main traveler in the cockpit. (The traveler was moved to the cabinhouse top on the 384.)
Despite these minuses, most owners cite the volume of the interior and many stowage compartments as major reasons for their satisfaction with the boat.
Performance Under Sail
As implied in our comments on balance in the “Design” section of this review, the centerboard 38 sailed beautifully. She is dry and seakindly, stable and relatively fast for her generation. Its PHRF rating ranges from 145 to about 150. The yawl rig is probably not as fast as the sloop, but for the cruising couple, the mizzen sail gives the skipper another means of balancing the boat, as well as a means to fly more sail when reaching if he’s prepared to fuss with a staysail.
The 382 rates between 128 and 150, about 137 on average. The Morgan 383 and 384, which are grouped together, rate a mite lower at 135, on average.

It is not surprising that Brewer’s redesign is faster, even though it’s 1,000-2,000 pounds heavier. This is due to it’s deeper fin and higher aspect rig with the ability to carry larger headsails. There is also less wetted surface.
Performance Under Power
The centerboard 38 was powered by the seemingly ageless Atomic Four gasoline engine, though a Perkins 4-107 or Westerbeke 4-107 was available at extra cost ($1,940 in 1969). The early 38s cruise at about 6 ½ knots.
A first-generation Yanmar—the 3QM30—was used on some 382s, and as owners of those engines know, they tend to be noisy and vibrate a great deal. Yanmar engines improved a great deal after the manufacturer redesigned and retooled the entire line. But the most common powerplant was the magnificent 50-horsepower Perkins 4-108. If we were looking for a Morgan 38 to purchase, we’d certainly lean toward one with this engine.
Both designs handle reasonably well under power, as well as most sailboats do, meaning that backing down with a two-blade prop is a necessarily cautious procedure.
A number of owners recommend changing to a three-blade prop, but that will affect sailing performance. One should examine his sailing style closely before making the move.
Conclusion
The Morgan 38, in any incarnation, is a handsome boat that sails well and is built strong enough for most people’s purposes. Some may pause before taking a centerboard boat far offshore, but it has certainly been done—recall, if you will, Carleton Mitchell’s hugely successful racer Finnisterre.
Both centerboard and fin keel versions seem to us to have advantages and disadvantages that are essentially tradeoffs.
On the one hand, we like an attached rudder for cruising, as it provides the best protection from collision with logs and other hard objects. On the other, we recognize the importance of placing ballast low, as in the fin keel version, and we appreciate
Brewer for giving a nice slope to its leading edge so that damage from hitting logs will be minimized. Brewer said that a 382 that passes survey is capable of cruising just about anywhere. “They’ve crossed oceans,” he said.
To our eye, we admit to being fond of the CCA designs with low freeboard and graceful sheer lines. The yawl is a versatile rig that is especially attractive, though it does require more in the way of tuning and maintenance.
An early Morgan 38, in good condition, should sell in the high 20s. Expect to pay a thousand or so more for the yawl. For sellers, considering that in 1969 the base price of the boat was $22,995, that’s not a bad return on investment.
Fifteen years later the price had jumped to $84,995 (1984 model). Those boats today are advertised in the mid to high 60s, and occasionally the low 70s. (What anyone is actually getting for these days is another matter entirely).
Considering the changes in the economy, that’s still not bad performance. What it means most to the prospective buyer is that the Morgan 38 and 382 are popular, much admired boats that should, we expect, hold their value as well as or better than most others.

































My husband & I bought a 382 Morgan in 1980. Named her Galewynd. We enjoyed her til we sold in 2000
My husband & I bought a 382 in 1980. We named her Galewynd. We enjoyed her til we sold in 2000