It’s hard to mistake the Stiletto 27s appearance-typically with blazing topside graphics and aircraft-style, pop-top companionway hatches. It’s also hard for the average sailor to appreciate the sophistication of the Stilettos construction-epoxy-saturated fiberglass over a Nomex honeycomb core.
Florida-based Force Engineering was formed to build the Stiletto in the late 70s. Forces then marketing director, Larry Tibbe, had been an aircraft account salesman for Ciba-Geigy, which manufactured Nomex. Nomex coring is used in a variety of aircraft parts (like helicopter blades), as well as the Stilettos hulls.
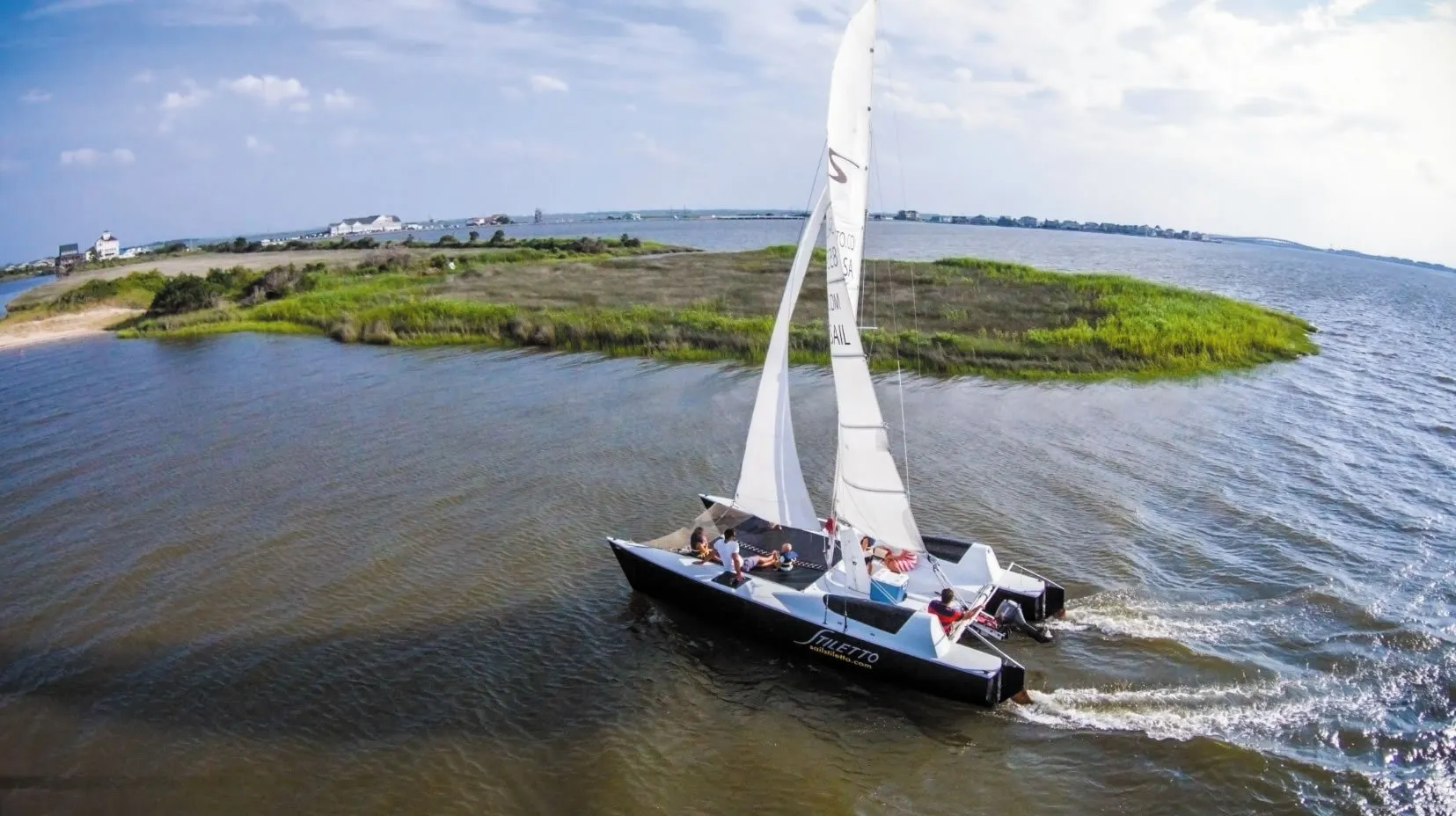

The 27, or Stiletto Classic, was offered in several versions. The Standard Stiletto had a mainsail, a nearly naked interior, and no options. The racing version, the Championship Edition, came with a few options like deck hatches, rubrails and removable berths, plus extra racing sails, winches, and a knotmeter. The Special Edition, the most expensive of the three, was equipped with pocket-cruising options like a galley, head, berths, carpeted interior, and running lights. The GT (Grand Tourismo) model came with daggerboards in each hull rather than a centerboard (as did the Stiletto 23 and Stiletto 30).
About 500 Stiletto 27s were built during the 10-year production run from 1976 to 1986, and most were Special Edition models; only six boats were GTs. However, like most older boats, custom buyer options and owner modifications over the years mean current Stilettos can vary widely in design details, deck hardware, sail options, rig sizes, etc.
Force engineers (and brothers) Ron and Andy Nicol bought the Stiletto brand in 1983 and continued to build new boats until 1986. After production ceased, the Nicols Stiletto Catamarans became a supplier of Stiletto parts and offered refurbishing and modification services. Recently, the Nicols partnered with the North Carolina-based Stiletto Manufacturing, which was founded by Jay Phillips to re-launch Stiletto boatbuilding. Stiletto Manufacturing has just begun producing the new Stiletto X-Series boats. (See Stiletto Foiler on Horizon accompanying this article on right.) Stiletto Catamarans, which continues to offer parts and services for the classic Stiletto models in Venice, Fla., will be regional distributors for the new X-Series boats.

Photos courtesy of Sail Stiletto and Ben Appel
Classifying Cats
Multihulls larger than 20 feet can usually be classified as cruising or performance boats. The cruising multihull is characterized by beamy hulls, with a cabin house across the bridgedeck, stubby rigs, monohull-like displacements, and spacious interiors. Their design priority is comfort. Performance multihulls feature light displacement, powerful rigs, and lean interiors. Custom ocean-racing trimarans fall into this latter category, as do a few production catamarans like the Stiletto 27.
The 27 has become a popular choice for owners looking for a more affordable option for multihull class racing. You’ll find active fleets of 27s racing in many parts of the country, but they’re likely most popular in Florida, the birthplace of Stiletto. In fact, the Stiletto Nationals are annually held in PSs homewaters of Sarasota, Fla.
While the Stiletto does offer ripping speed, its also a good family boat. Its trailerable and beachable, making it a fun platform for weekend camping trips aboard or exploring desolate beaches and sandbars with the kids. It doesn’t have the creature comforts of a typical cruising cat, but for a low-maintenance crew, it makes near-shore and inshore cruising accessible. It offers a stable ride and can easily accommodate six to eight people on deck. Its also a forgiving boat for new multihull skippers or sailing newbies; with only 9 inches of draft (centerboard up) and weighing only 1,100 pounds, there’s no need to worry about soft groundings as it can easily be pushed off the bottom.
Construction
Very few boats are cored with the Nomex honeycomb that make up the 27s hulls and bridgedeck. Sandwiching a core material between two layers of fiberglass laminate is not a new technique, but most boatbuilders use cores of balsa wood, Airex foam, or Klegecell foam. Core construction offers several advantages over single-skin construction. It is stiffer for a given weight, lighter for a given stiffness, makes the boat quieter, and reduces condensation.
Honeycomb is rarely used for boatbuilding because the molding procedure is far more sophisticated (and expensive) than with balsa or foam cores. Honeycomb can be made of several materials: paper, aluminum, and nylon. Using paper or aluminum honeycomb in boats is questionable because of their susceptibility to water damage should the cores outer laminate be breached. However, the Stilettos Nomex honeycomb core is made of nylon.
According to Stiletto, a Nomex honeycomb-cored panel, for a given weight, is stronger, stiffer, less brittle, and more puncture resistant than foam or wood cores. Nomex is also said to be impervious to water, so there is no water migration between the honeycomb cells should the outer skin be ruptured.
Getting the honeycomb to bond to the fiberglass skins isn’t easy. First, the fiberglass cloth must be pre-impregnated with epoxy resin. Most boat builders use polyester resin, which lacks the adhesive strength of epoxy, and saturate the fiberglass after it has been laid into the mold-a messy and inexact procedure. Pre-impregnated cloth, or prepreg, has an exact resin-to-cloth ratio, which means that the builder always has the optimum strength-to-weight ratio. Most boat builders must err on the resin-rich side when saturating cloth, which increases weight but not strength.
To cure the prepreg after layup, the mold was baked at 250 degrees for 90 minutes. At the same time, the fiberglass skins were vacuum-bagged to the honeycomb to ensure proper adhesion.
Most builders vacuum-bagging process entails laying a sheet of plastic into the mold and sucking the air out with a single pump. Force Engineering used a blotter to absorb excess resin and 16 spigots to distribute the vacuum, a more effective technique. When finished, each of the Stiletto 27s hulls weighed only 220 pounds and was impressively strong and stiff.
Unlike the high-tech hull and bridgedeck, the aluminum mast and crossbeams were built with conventional technology. All-up, the Stiletto weighed 1,100 to 1,570 pounds, depending on optional equipment.
Gelcoat cannot be used in the Stilettos molding process. Instead, each boat must be faired with putty and painted with polyurethane. Paint has the advantage that it will not chalk like gelcoat and is much easier to repair yourself, but it is more susceptible to nicks, scrapes and peeling, especially if improperly applied.
Except for the handful of GT models, the Stiletto 27 was designed with a single centerboard mounted on centerline through a slot in the bridgedeck. It is held snugly in place by a latticework of stainless-steel tubes designed to collapse in the event of a hard grounding. The airfoil centerboard on older models was made of wood, and chipped trailing edges were a common problem. Later boards were molded of fiberglass and more resistant to damage.
Some performance-minded Stiletto owners have done away with the centerboard all together, opting instead for a high-aspect daggerboard in each hull, with added bulkheads to support the daggers. This increases the boats pointing ability and boosts overall performance.
Few Classics still have the original aluminum spars and crossbeams. Common modifications on the 27s include moving the forward crossbeam forward 18 inches (increasing overall stiffness and adding sail area in the foretraingle) and extending mast heights three feet to accommodate a larger, square-top mainsail. Many of these modifications, along with the daggerboard refits, were carried out by the Nicols at Stiletto Catamarans.
The Stiletto 27 gets high marks for its rudders. They have strong aluminum heads and double lower pintles. To be beachable, a catamaran must have kick-up rudders; these kick-up systems often refuse to work when you need them most. However, the Stilettos rudders worked smoothly and positively on the boats we test sailed.
Trailerability
One of the Classics selling points is its trailerability. But while it is light enough to be pulled by a vehicle with a tow capacity of 3,500 pounds (stripped-down racing 27s may get away with only 2,000 pound capacity, but wed err on the side of caution), rigging and launching the Stiletto is not a simple chore. Owners say it takes several people (two to four) several hours (three or four). To shrink the beamy (13 feet, 10 inches) Stiletto down to legal highway trailering width (8 feet typically), both the Stilettos crossbeams and the trailer collapse. The compression tube that spans the bows must be removed for trailering, as must the dolphin striker beneath the mast step and the 125-pound bridgedeck.
To raise and lower the mast, the headstay is shackled to a short, pivoting gin pole mounted just aft of the trailer winch. The winch is used to pull the gin pole, which in turn provides leverage to hoist the heavy mast. Owners say that lifting the bridgedeck and manhandling the spar is next to impossible with just a couple. As long as you have the muscle, this clever system does work.
Sailing
The Stiletto is a performance catamaran. In a breeze, owners report, she is as fast or faster than a Hobie 16. Most have been upgraded with genoas, drifter/reachers, and spinnakers. Many also sport deep reefs and storm jibs, required to keep the boat manageable in a blow.
According to owners, the Stiletto does not have some of the bad heavy-air habits of smaller catamarans. It is relatively dry to sail up to about 12 knots, does not hike up and fly a hull too easily, has no tendency to pitchpole, and does not get light as it comes off a big wave sailing upwind.
Like most cats, the Stiletto has a fully battened mainsail. The advantage is that it can have a much larger roach, and because the battens dampen luffing, the sail will last longer.
The Stiletto also has a rotating mast. The older masts have only athwartships diamond shrouds; the later 27s have an added third diamond extended forward to control fore-and-aft bend in a strong breeze. This three-diamond system is strongly welded together and a real plus for heavy-weather sailing.

Deck Layout
The Stiletto has a solid bridgedeck stretched between the two hulls aft of the mast, and a polypropylene mesh trampoline forward of the mast. You’ll find varying trampoline setups; some are laced with a series of hooks and others have bolt rope edges that slide into tracks on the hull and crossbeams.
The bridgedeck, which is where crew spends the most time, has no proper seats, but it does have molded-in benches running the length of each side of the bridgedeck. These are not the most comfortable for seating underway, but some owners have reported that using marinized beanbags for lounging is a practical option. Bridgedeck cushions were standard on the Special Edition, and many owners have added them over the years-some also have added a backrest for the helmsman.
A wire stretched between the bows forward of the headstay acts as a traveler for the optional reacher/drifter. Many owners have added roller-furling headsails and main halyard winches; headsail winches were standard on the Championship Edition but were an extra-cost option on the other models as sheet loads on such a light boat are not that high.
The Stiletto has a ball-bearing mainsheet traveler, but the original mainsheet setup had only a 6-to-1 purchase, which owners say is insufficient in a breeze; an 8-to-1 setup is recommended. The tiller extension passes behind the mainsheet, and the tiller crossbar is adjustable so you can align the two rudders. The jibsheets are led to ratchet blocks (Harken brand on our test boat) to make trimming easier.
The outboard engine bracket is hung off the aft crossbeam. Engines up to 18 horsepower are common on the 27s, giving motoring speeds of 12 to 14 knots, but a 6-horsepower outboard is adequate and more popular with racers.
Interior
The Standard Stiletto version is nothing but an empty shell below. The Special Editions original interior was completely covered-ceilings, overhead and sole-with marine carpeting. No doubt, most owners have removed the carpet by now, or at least replaced it.
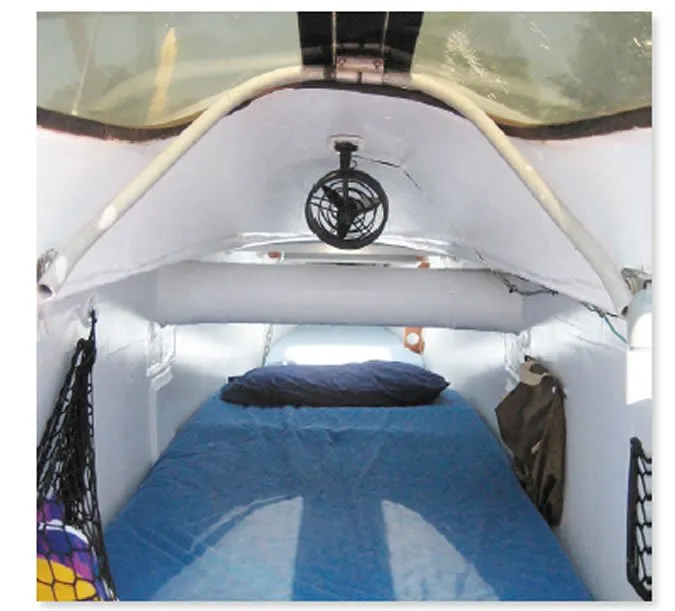
The Stiletto has the narrow hulls of a fast catamaran, which means that its berths are only 31 inches wide (twin size) but are extra long (14 feet), with one in each hull. There is stowage space under the berths.
Stilettos were offered with an optional mosquito-tight bridgedeck tent. Owners have reported that the tent was bulky and cumbersome, so most have ditched it in favor of popup tents set up on the trampoline or DIY boom tents over an air mattress on the bridgedeck.
The Special Edition had a self-contained head under one berth and a small galley with a sink, a hand-pump faucet, and a two-gallon water tank. There was no standard mounted stove, but many owners keep a portable stove onboard, which is more practical for this boat in our opinion. The Special Edition was also the only model with standard running and interior lights.
Perhaps the most distinctive feature of the Stiletto is its conical, jet-fighter-looking companionway hatches. The canopies are vacuum-formed polycarbonate. These canopies can’t be cracked open like a conventional hatch, so it can get stuffy down below when its raining.
Conclusions
There is probably no production hull built in the U.S. with a better strength-to-weight ratio than the Stiletto. And although the design is 40 years old, the Nomex honeycomb fabrication is still impressive.
The Stiletto seems to appeal to the catamaran sailor hooked on fast performance, but who wants a boat that be taken places-either sailed to nearby weekend destinations or trailered out of state for a race or getaway. There are other options with more creature comforts for the multihull sailor who wants to weekend cruise, but few in this size and price range can offer the same speed performance and trailerability.
As PS contributor and former Stiletto 27 owner Drew Frye put it, How many $10,000, 40-year-old designs can top 20 knots with just Dad and a 10-year-old for crew, and then pull up to the beach so you can look for crabs with your kid?
If you’re considering a used 27, the ones in ready-to-sail shape run $15,000 to $25,000, but they hold their resale value. Replacement parts can still be bought from Stiletto Catamarans, and there is a very active and knowledgable owners group online.
The Stiletto 27 is certainly a niche boat-somewhere between beachcat and performance cruiser-but it serves that niche well, as its 40-year history can attest.

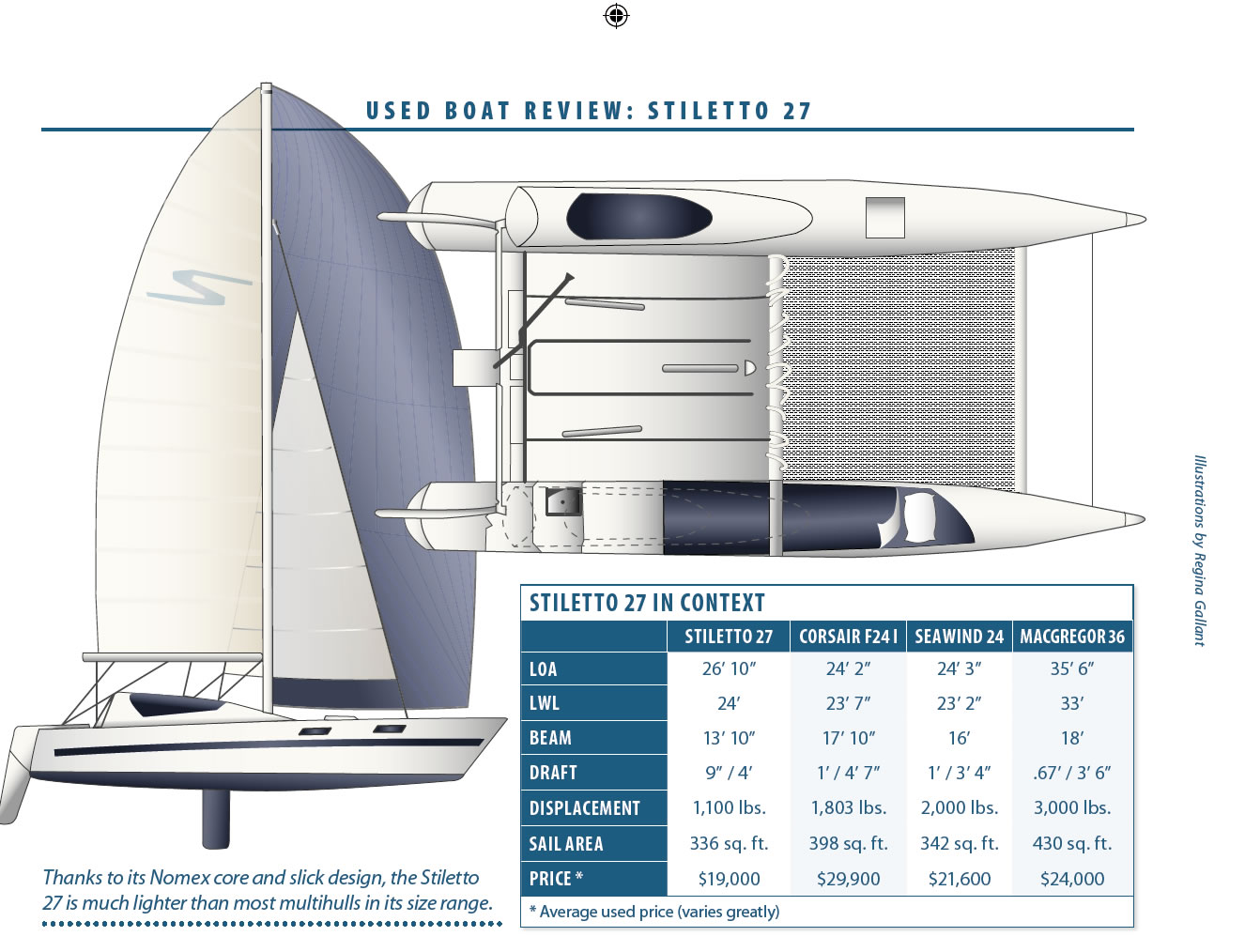
Thanks to its Nomex core and slick design, the Stiletto 27 is much lighter than most multihulls in its size range.




































I had a 27′ Stiletto. Took it to the nationals and trailered it everywhere.
I would do it again, if my wife would let me
Get another wife!
I worked for Hawaiian Tropic and sailed the 23 and 27 for 9 years loved both . Sucks I had 2 stroke’s recently and have been looking in my area for one.
Should get back pay soon watch out!