This fast and handsome cruiser/racer from the 1970s is an excellent example of what made C&C Yachts such a successful company. C&C stands for George Cuthbertson & George Cassian, the design team that, in 1969, joined in partnership with Belleville Marine Yard, Hinterhoeller Ltd. and Bruckmann Manufacturing to form C&C Yachts. The company had a tumultuous history, from growing to capture an estimated 20 percent of the U.S. market during the 1970s, to suffering a devastating fire in 1994 while owned by Hong Kong businessmen Anthony Koo and Frank Chow of Wa Kwang Shipping. Along the way, they built a tremendous number of boats, not only in the racer/cruiser genre that was their mtier, but also the Landfall cruiser line, and a few oddballs such as the 1977 Mega 30 with a retractable fin keel; the Mega 30 and a handful of others simply bombed.
Most boats were built at one of several Ontario, Canada, facilities, but short periods of construction also took place in Middletown, R.I., and Kiel, Germany. In 1998, Fairport Marine, which owned Tartan Marine, purchased the C&C name and some molds and moved the remnants to Ohio. Other than the name and the emphasis on performance, however, there is no tangible connection between that more modern C&C and the giant of 25 years ago that so dominated the North American yachting scene.

The Design
The C&C 27 followed quickly on the heels of the successful C&C 35. The design dates to 1970, with the first boats coming off the line in 1971. C&C tweaked the design through four versions of the original 27-the Mark I, II, III and IV-but the hulls were very similar. The C&C 27s production ended in 1982 after nearly 1,000 had been built. From 1984 to 1987, C&C offered the Mark V, which was an MORC-influenced 27-footer with an outboard rudder; its design strayed far from the Mark I, II, III, and IV, and it should not be confused with the previous editions.
The 27 is a good example of what made C&C successful-contemporary good looks with sharp, crisp lines that still hold appeal today. The sheerline is handsome. Below the waterline, the swept-back appendages are dated, but thats of little significance to most owners. In the Mark I version, the partially balanced spade rudder is angled aft, with a good portion of it protruding behind the transom. In one of his reviews for Sailing magazine, designer Robert Perry described the C&C 27s rudder as a scimitar shape that was long in the chord and shallow. In 1974, when the Mark IV was born, the rudder was redesigned with a constant chord length and much greater depth and less sweep angle.

The keel, too, was redesigned in 1974, though most were swept aft like an inverted sharks fin. The Mark IIIs keel was given 2 inches more depth and the maximum thickness was moved forward to delay stalling. Hydrodynamic considerations aside, the worst that can be said of the 27s keel is that it takes extra care in blocking when the boat is hauled and set down on jack stands. Without a flat run on the bottom of the keel, the boat wants to rock forward.
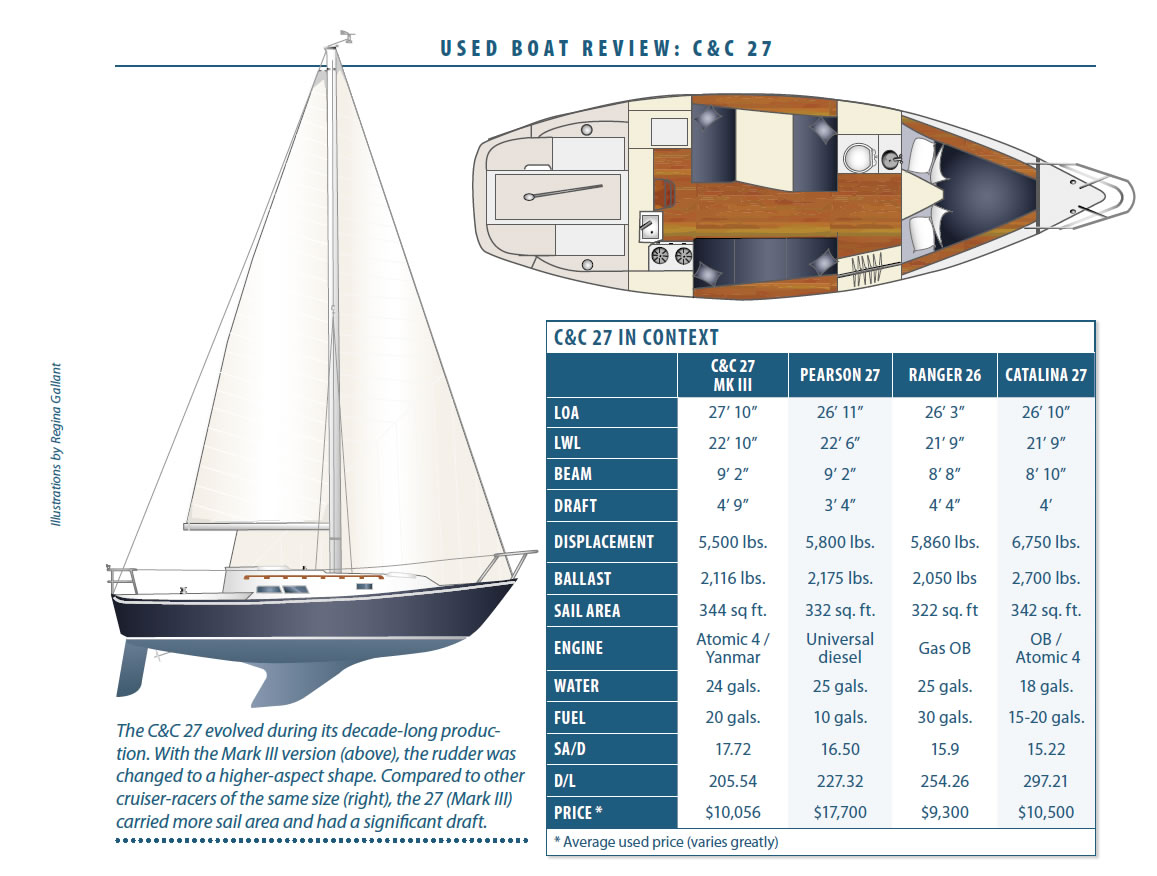
Through its evolution, the C&C 27 not only gained draft, but it gained length overall as well: Both marks I and II were 27 feet, 4 inches long (21 feet at waterline), while marks III and IV were 27 feet, 10.5 inches from stem to stern (22 feet, 11 inches at waterline). The bow overhang is attractive, but more than what is found on most boats nowadays. Remember that waterline length directly affects speed.

All editions have a 9-foot, 2-inch beam, but displacement changed over the years-from 5,180 pounds to 5,500 pounds and then 5,800 pounds. And with the Mark III, the design shed about 400 pounds of ballast.
The later models rigs were masthead sloops with a mainsail luff length (P) of 28 feet, 6 inches and a foot length (E) of 10 feet, 6 inches; this gives an aspect ratio of .36. Rig height on the Mark I was 33 feet, and the Mark II had a 35-foot-tall rig.
Depending on which waterline dimension you use, the displacement/length ratio (D/L) ranges from 211 to 237. The sail/area displacement ratio (SA/D) is between 17.3 and 19.4. With moderate displacement and a generous sail plan, the C&C 27 is swift. PHRF ratings for the Mark I average around 200 seconds per mile, dropping to about 195 for the Mark II and 180 for the Mark III.
According to the C&C 27 owners association, C&C Yachts used only the Mark I and Mark II designations-the first for the original hull-form and the latter for a stretched and subtly reshaped development from the original. However, C&C 27 sailors added the other designations to distinguish between the different models, particularly for racing ratings.
About half of the C&C 27 owners use the boat strictly for cruising, while the other half also enjoy some club racing aboard the boat. Racing fleets are larger in Canada than the U.S., but they can be found in significant numbers on the West Coast and in the Great Lakes as well. There is a rather active owners association, and the groups website (see Resources) offers technical information, manuals, links to vendors for C&C 27 parts, as well as a forum for owners Q&A.
For more on the differences between the various models, see the accompanying The Evolution of the C&C 27 Cruiser-racer.
Construction
C&C Yachts was a pioneer in balsa sandwich construction, but the early C&C 27s had solid-glass hulls. Decks were balsa-cored. An old brochure says the marine-ply bulkheads are taped and bonded to hull and deck, though photos show a headliner, which seems to make deck tabbing not possible. The same brochure says fiberglass is hand-laid-up, using alternate layers of mat and cloth; no mention is made of woven roving, which is commonly used to add thickness quickly.
During this period, C&C used a molded fiberglass pan that incorporated the cabin sole and berth foundations, but did not extend higher. The berth/settee backs, and galley and head cabinetry are plywood, and access to parts of the hull is generally good.
Ballast is an external lead casting through-bolted to reinforced hull sections.
In our survey of C&C 27 owners, one owner said that the cabin sole needs supporting timbers underneath. One trick that C&C used in lieu of floors was to lay in thick bands of fiberglass athwartship (about 6 inches wide). These started on one side of the hull, crossed the bilge, and went up the other side.
A C&C trademark was the L-shaped aluminum toerail with slots for attaching snatch blocks. Of equal benefit was the ability to use carriage bolts for the hull-deck joint, which could be installed by one person rather than two. Other builders quickly copied this feature.
For weekending and coastal cruising, there is a lot to like in the light, rigid C&C 27, but many C&Cs have weak spots that would need to be addressed for offshore work: bulkheads not tabbed to the deck (which may result in the deck lifting as the boat and rig work); thin laminates in the outboard edges of the sidedecks where stanchion bases are bolted; absence of backing plates on pulpits; and thin portlight lenses that should be replaced or fitted with storm shutters.
And, as with any older boat, prospective buyers should check for bulkhead rot where the chainplates attach (water runs down the plate and through the deck, which is difficult to seal) and for delamination of the decks, especially around hardware, whose bedding may have disappeared years ago. Rebedding deck fittings is a boring job, but a very important one because the balsa core is at risk. It is made easier-and less boring-if you have a helper (one of you on deck, the other below). You don’t have to do everything the first year; start with the worst fittings and do them in groups, at least a few each year.
Interior
Twenty-seven feet is in many respects a magic number for a sailboat. At this length, it is possible to have standing headroom without distorting the boats proportions beyond all good taste, and to have an inboard engine, with its obvious advantages and status. Headroom around the 27 is between 5 feet, 10 inches and 6 feet, 2 inches.
The accommodation plan is plain vanilla, tried and true: 6-foot-plus V-berth forward, head and hanging locker, dinette with opposing settee, and aft galley. Without a quarterberth, the 27s cockpit seat lockers provide valuable and generous stowage for lines, fenders, barbecue and cleaning supplies, and all the other stuff that goes with sailing.
Testers liked that there is a bridgedeck, which we think is a sensible choice as it a) helps keep water out of the cabin in the event the boat is pooped; b) provides additional seating in the cockpit; and c) offers additional space in the galley.
A lot of C&Cs were not particularly well ventilated, and the 27 is no exception. The big windows in the main saloon are fixed. Most air will enter from the forward hatch, which on a small boat in northern latitudes may be adequate, but hardly ideal for southern sailing. A dorade vent over the head was an option.

Performance
The C&C 27 was one of the companys most popular designs, and much of this was due to its smart handling and good turn of speed. Not surprisingly, owners generally rate its upwind and off-the-wind performance as above average.
Several owners we surveyed said that light air is the Mark Is Achilles heel and that a large genoa of more than 150 percent is necessary to stay competitive. In 1974, the rig was lengthened 3 feet and sail area increased from 348 to 372 square feet.
The boat handles easily. Turns 360 degrees within its own length, said one owner of a 1973 model.
Extremely well balanced, wrote another owner.
The only negative comment made by owners concerned increasing weather helm as the wind builds; they advised reefing early. The owner of a 1971 model explained, The Mark III has a high-aspect rudder; the original rudder gives the boat extremely bad weather helm.
Points very high, wrote the owner of hull No. 146. Shes easily controlled off the wind. If sail is reduced intelligently, shes a dream to drive. Rock solid at about 18 degrees.
Early models featured mainsheet sheeting at the end of the boom, but in 1974, the standard setup was changed to mid-boom sheeting with the traveler on the bridgedeck.
The 27s auxiliary power ranged from an Atomic 4 gasoline engine to a two-cylinder Yanmar diesel. Most owners have reported that their boats back up beautifully. Best backing boat Ive seen, said the owner of a 1977 model. Comments on engine accessibility also ran the gamut, ranging from easy to ridiculous-which may say more about the size of the respondents than anything else.
Conclusion
With prices ranging from $10,000 to $20,000 (some with a trailer), the C&C 27 represents a fair value-standing headroom for most, berths for four (owners say the dinette is a bit narrow for a double when converted), and an inboard engine. The Yanmars of the late models are preferred over the old Atomic 4, but many of the boats on the market today have been re-powered.
Potential buyers should pay particular attention to the pulpit and stanchion bases and the surrounding fiberglass for signs of cracks; and check the deck core and the interior support structure that handles mast compression for signs of rot.
Boats built after 1974 (Mark III) seem to sail better thanks to the incorporated refinements-new rudder, deeper keel, taller rig, added shrouds, etc.
Of the many owner comments weve heard about the boat, one in particular rings particularly true: Simple systems, easy to maintain. That means owners wont spend an arm and a leg trying to keep the C&C 27 afloat, and that has a great deal of appeal for us.