As a longtime multihull sailor I’m often told that it must be wonderful to anchor wherever I want and tuck into the smallest of coves. Yes, there is some truth to that. An owner of a Phillip Bolger-designed classic leeboard Dovekie once bragged to me that his boat would float “on heavy dew.” But in the next breath he related a hellish experience cutting across a shallow that extended nearly one mile off a lee shore. A reasonable 2-foot chop in deeper water became 3-foot breaking waves. So let’s break it down.
Beaching
This is the big myth, so let’s bust it right now.
You better enjoy bottom painting. Every time the bow shifts, you sand off a few grams of $200-per-gallon paint. Even beach cats use wheels because repeated hauling will grind the gelcoat right through in season or two. I’ve reglassed bottoms because of this.
Rudders are at high risk. Backing off is the obvious problem, but getting knocked sideways by a wake is worse. I’ve seen rudder cassettes split open.
Beware of ferries. If a ferry comes along, the wake can leave you high and dry. It hasn’t happened to me, but I’ve watched people spend days trying to refloat a boat.
You still need to set an anchor. If the wind shifts, the tide rises, or a wave knocks you sideways, the boat can sail away. Been there, done that. So anchor out within wading distance if you can. Dry bags are terrific help if you are planning a beach camping trip.
Beaching is for lighter boats only. It is only acceptable if you can lift and carry to the high waterline. Snuggling the bow up to a sandbar and reclining on the sand with a cold drink is romantic in advertisements, but if there is enough wind to sail, it is a bad, awful idea. Only boats that can be hauled securely up the beach should be beached.
Allow for tide. Sure, you can anchor in just a few feet, but if the tide drops you will either be stranded or pounding up and down on the bottom. And what if there are a few scattered rocks or tree trunks? Just like deep draft boats, you need to allow for tide and a safety factor.
Waves and wakes are worse in the shallows. Up a small creek you can anchor in 3 feet, but in an open roadstead or even a harbor with long fetch or heavy traffic, 6 to 8 feet is a healthy minimum, just based on wave action.
Gotta have a snubber. Chain catenary depends on the amount of chain deployed. In deep water—20 feet or more—even relatively short scope puts 120 feet of chain in the water. The same boat anchored in 4 feet would deploy as little as 35 feet of chain, and the waves will hit like a hammer.
Even worse is the onset of hobby horsing; short steep waves will get the bow moving vertically, and with no catenary, that’s a good formula for popping out an anchor. I’ve often anchored in shallows with only 70 feet of chain out, but even in good shelter I attached a 20-foot snubber at the 50-foot mark. Any less is asking for snatching when a wake hits. I once measured a 2,200-pound jolt on my chain rode when a power boat wake rocked the boat just wrong.
If you are planning to spend the night on the boat, close to the beach might not be the most pleasant spot to anchor. During summer, bugs are horrible within 200 feet of shore, even more so if you plan to cook. If I pull up close to shore to allow easy wading, I’ll still move out a good distance for the night.
Sailing
Avoid lee shores. The most dangerous case is a rocky shore, certain to break the boat into small pieces and put the crew at risk. But a shoal-draft sailor can be tempted to sail in the shallows off a beach or over a sandbar.
In just 3-5 feet of water, even moderate chop turns steep and nasty. If the board touches bottom in the troughs, things quickly get dicey. If you leave the board down, the boat stops and the board takes a beating. If you lift the board to get moving and prevent damage, you make leeway, can’t beat off, and soon touch bottom again. The motor will bounce up and down, ventilating, risking damage, and providing little push. It may not look life threatening (it can be), but it can get expensive even in just 10 knots.
Waves will push you around. If the keel isn’t into solid water under the wave, there is a tendency for waves to push you to leeward. Low aspect keels aren’t just hydrodynamically inefficient, they are also handicapped by working in moving surface layers. For shallow keels to work, they must be sailed fast, like a beach cat. Slow them down and they just don’t point in waves.
Kick-up rudders

anywhere. The Venture 21 can float in less than two feet of water, but it needs at
least three feet to be sailed, and about four feet to point best (see PS April 2011).
Once the rudder is up, you’re done sailing. If it kicks back, the leverage is horrible. If you can raise the rudder, it still won’t have enough bite. I learned to sail on beach cats, and lacking deep keels, they rely on deep, efficient rudders for a good portion of their lateral resistance.
Centerboards and daggerboards are wonderfully efficient to windward, with low drag and high lift if sailed in the pocket. A centerboard-equipped F-24 trimaran can sail circles around a mini-keel PDQ 32 catamaran, but it also draws 5 feet versus 3.5 feet. The F-24 draft can be reduced to 18 inches by lifting the centerboard, but even while motoring the steering becomes mushy.
If the board is left down and allowed bump, it will wear, and there is risk of hinge and structural damage. Damage to dagger boards can be sudden and catastrophic if the boat is moving more than 5 knots. You can lift the boards halfway, but the result is a compromise.
Larger “Condomarans” prove the importance of balanced design by employing all of the performance limiters in one package: house trailer windage, low aspect-ratio keels, tiny rudders, and too little canvas. You just can’t make that work.
Low-aspect ratio keels can create boats that are terrible at tacking. Specific to cats, you have two long hulls, with minimal rocker, that must be dragged around a 90-degree turn. Add poor pointing angles, low speed, too little sail area, and too much windage, and you have a tacking slug. The solutions?
- Good speed. Never tack from anything other than full-and-by (close hauled but no fluttering). Since most of these boats do not have a backstay, keep the mainsheet tight (that is your backstay).
- Weight back during the tack. On beach cats and performance multihulls, lifting the bows reduces drag through the turn.
- Ease the traveler and mainsheet. Once the jib breaks, ease the main enough that it does not push the boat back into irons.
- Release the jib when it breaks. There may be some benefit in holding an overlapping headsail just long enough so that it blows through positively, but do not delay so long that the backed sail slows the boat.
- Get the jib in quick. There is no excuse for not having it trimmed in the moment it first can fill on the new tack. It will pull the bow through and help the boat accelerate. If something is snagging, remove the cause of the snag.
What about backwinding the jib? Only when proper technique fails. If the boat fall into irons, slack the main completely, use the rudder to back up in the opposite of the direction that you wish to go, and let the boat fall of onto a beam reach before you make any attempts to sheet the main in and go start forward. Sheet in gradually.
Marinas
This is where the benefits of shoal draft kick-in. Shallow berths are cheaper in some markets. Deep water slips rent for a premium. Often marinas have shallow slips along the bulkhead or in some corner.
But taking the ground on a low spring tide is a risk. Mud is best, sand is no good, and checking for debris under the slip is a smart move.
Maintenance
It nice to be able to work while wading instead of swimming, with caveats.
Scrubbing. Hard paint can be scrubbed, but soft paint rapidly wears away, polluting the environment and fouling even faster (“Bottom Paint Care,” PS March 2018). And scrubbing while wading is not that much better than swimming, because the boat is constantly yawing in the wind. When you push, the boat swings away from you, so you are constantly walking. Sometimes the motion is faster than you can walk.
Mechanical work. I’ve replaced outboard lower units both ways, and floating in a PFD was easier (float your tools in a mortar tray). Small multihulls can lace trampolines in the shallows, but if you plan it out, it’s actually easier in a marina.
Drying out to paint is a myth in most places. There isn’t enough tide. You won’t have time to scrape, and in this day, you must capture everything that comes off the boat. And what about paint drying time?
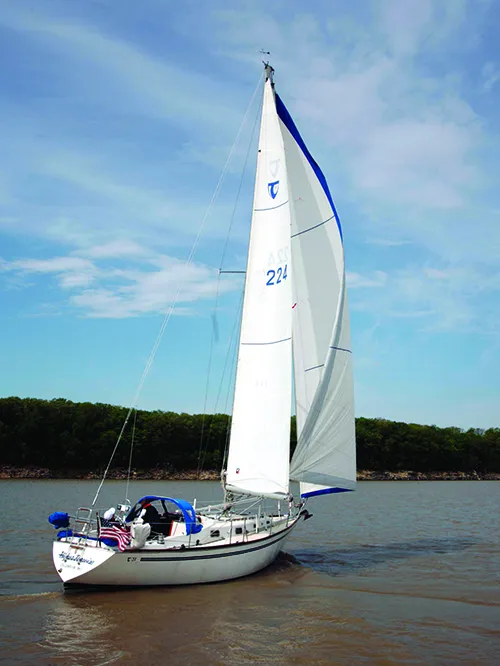

designed Tartan 37 can race, cruise
and gunkhole like few mid-size boats.
In the market for a centerboard cruiser? Here is my take on very short list of 35- to 45-foot boats that have drawn my eye. Some I’ve sailed, some not. I’d love to hear from readers about their favorite centerboarders.
Krogen 38
This is a pure cruising cutter that the late Jim Krogen designed for himself to cruise the shoal waters of Florida and the Bahamas. It has two bronze centerboards, one in front of the other, making it very easy to balance on long passages.
Pros: This is a robust, three-cabin cruising boat with a loyal following.
Cons: Cored hull and teak decks on the boat often pose problems.
Morgan 41 Centerboard
I’ve sailed on a couple of these sloops and like the way they look and sail. The poor man’s Bermuda 40’s heritage traces back to designer Charlie Morgan’s breakthrough Paper Tiger, ensuring a loyal following among Morgan fans.
Pros: Storied design, with a good deck layout and comfortable motion.
Cons: Finish quality varies greatly as many were owner-completed. Factory interior is pretty basic.
Tartan 37
A classic Sparkman & Stephens design. Three couples who I cruised in company with in the Caribbean had Tartan 37s, and all of them were happy with the boat.
Pros: A very popular dual-purpose classic with good bones.
Cons: A bit pricey for the size and vintage, and not as spacious as contemporary 37-footers.
Ovni 43
In the Pacific and Southeast Asia, we sailed with two different couples cruising aboard these aluminum boats, made popular by circumnavigator, rally organizer, and author Jimmy Cornell.
Pros: Tough aluminum construction, good track record.
Cons: High price, and used boats are hard to find.
Block Island 40
I’ve never sailed on this fabled yawl designed by Bill Tripp, but contributing editor Ralph Naranjo often cites it as an example of rugged construction and sound design.
Pros: Proven offshore design with a cult-like following.
Cons: Many of the older Block Island 40s require expensive upgrades that will quickly eat through a cruising budget.
Bristol 35.5
This Ted Hood design marked Bristol’s push into the big-boat market under Clint Pearson.
Pros: This is a solidly built and popular Bermuda veteran.
Cons: Totally enclosed cable makes it difficult to service. Not as spacious as contemporary cruisers in this size.
Sabre 38 MkI or MkII
I’ve sailed several Sabres, ranging from the older Roger Hewson designed 34s to the new-generation Jim Taylor boats, and have always been impressed with the way they handled.
Pros: Sabres craftsmanship is above average for production boats. Stick-built interior is more amenable to owner conversions.
Cons: Outside of the Northeast, Sabres do not carry as much value as some other brands.
Some of the myths are true, or I wouldn’t have stayed with multihulls. I can take a short cut over the 4-foot bar in front of my home marina, shaving several miles off the deep keel parade around the end. I can avoid the crowds, anchoring in creeks and coves too shallow to merit guidebook mention. My slip is cheap; all of the sailboats in my marina are multihulls. I regularly anchor within wading distance of the beach. It is tons of fun in the summer.
Being able to duck inside, between barrier islands is handy when the weather turns grim, but never try a shallow inlet in onshore conditions; you need to make this decision before it begins to break.
I took several long trips with my young daughter around the Delmarva Peninsula, often taking the notorious shallow and fickle Virginia Inside Passage. It is a memory neither of us will forget. And isn’t that what boats are all about?









































Why don’t you build flying sail boats insread of the way they built them in 1492
Foiling is fun! However, you never foil or even sail fast in shoal waters; grounding with a board or foil at over 10 knots gets expensive really fast. You slow down to keel boat speeds and lift the boards as soon as the bottom gets close.
Would you say these comments apply to smaller monohulls as well? Sub 20 feet? The Dovekie, included in your opening paragraph, is an example it has pivoting leeboards, small bow centerboard and a pivoting rudder. Draws 4 inches fully retracted and weighs about 600 lbs. The boat could be pulled up on the beach using inflatable rollers but may not be necessary with 4 inch draft. I think most of the anchorages would be very secluded with little chance of fetch or wake building waves. Maybe hull maintenance isn’t so bad on such a small vessel? Clearly, they need to choose conditions and maybe that’s difficult when conditions can change after the decision has been made. Your opening paragraph highlights the weather trouble.
Dovekie owners often say they will “float on heavy dew.” That’s a stellar trait in many estuaries.
Yes, you can pull many small boats up on the sand without aid from rollers. I can assure you, though, that 600 pounds of flat bottom will be a burly task, since a 350-pound Hobie cat takes two. Additionally, you will grind off some gel coat in the process. My first fiberglass repair experience was rebuilding the keels of a beach cat that had been hauled up too many times. After that, I used beach wheels. Yes, small creek beaches can be safe, but wavelets in even the best sheltered cove will cause the boat to sway and grind on the beach unless anchor out or carry above the influence of the waves, and don’t forget that the tide will change, leaving the boat adrift or high and dry. Every dinghy operator has experienced this.
We really like little boats. We just wanted to inject a little realism and help users avoid a few of the pitfalls we have stepped in.
So, for extreme shoal draft, sheltered anchorage with 2 feet below keel at low tide. Does that sound safe? Wavelets wouldn’t be a problem then. I do appreciate the warning on breaking waves in shallow water. I’m trying to decide on a trailer sailor for my family and weighing the difference between an extreme boat like the Dovekie or some thing a bit more conventional like the CLC Pocketship. We are comfortable in tents. Seems like the Dovekie would give us more of what we want but we would still need to follow sensible anchoring guidelines.
I’d like to direct you to a local Dovekie owners group at http://www.shallowwatersailor.us. They have a lot more experience with these specific boats than I do. You may be on the right path, but it just depends on where you sail and what you like.