Photos by Gerry Hutchins
Com-Pac Yachts is a Florida boat builder with a particularly interesting history. The company was formed in 1957 by W. L. Hutch Hutchins Sr., an entrepreneurial tool-and-die maker who operated a metal-stamping and fabrication shop in St. Louis, Missouri. A successful inventor, he created everything from automobile accessories, including the Ah-ooo-gah horn often retrofitted on Model A Fords, to a unique folding high-chair.
In 1970, Hutchins converted a personal interest in sailing into a corporate endeavor when he commissioned Clark Mills to design the Com-Pac Yacht, a 16-footer capable of being shipped in a box. Mills is most famous for designing the Windmill and Optimist prams. Hutchinss goal was to build a small but highly efficient sailboat that could easily be trailered behind a compact car.
The first boat, constructed in 1974, was trailered by Hutchins behind a Ford Pinto. The company eventually introduced several small models, ranging in size from 19 to 23 feet. Bob Johnson of Island Packet and Charley Morgan were employed as designers of the companys three cruisers, the Com-Pac 25-, 27-, and 35-footers. A line of catboats was introduced in 1999, and the companys production has since shifted in the direction of these and other smaller boats.
Com-Pac loosely categorizes its boats into four classes. Its trailerable catboats include the 14-foot Picnic Cat; the 17-foot Sun Cat (available in three configurations-a full cabin, a cuddy cabin, and an open cockpit); and the 20-foot Horizon Cat, based on the classic Cape Cod catboat design (also available with a larger cockpit, and renamed the Horizon Day Cat). Its trailerable sloops include a 16.5-daysailer called the Legacy and the Com-Pac Eclipse, a 21-foot micro-cruiser.
The only Com-Pac cruiser listed on the companys website today is the Com-Pac 27/3, a 6,000-pound-displacement coastal cruiser, but Com-Pac still has the molds to the 35. A lack of orders in recent years has led to some discussion about dropping the design from the lineup, but for now, it remains in production.
Brothers Rich and Gerry Hutchins now run the company. Rich has worked for Com-Pac since his childhood, once running the metal shop in St. Louis. Younger brother Gerry is a graduate engineer who began his career at Gulfstar.
The Com-Pac 35 is regarded as a semi-custom boat, so owners are allowed some latitude in selecting the accommodations. Production is limited to four to or five boats per year, but it has been several years since they have had any orders, according to the maker. The bulk of Com-Pacs boat-building orders these days are for the smaller daysailers. During its peak production run, the Com-Pac 35 represented about 25 percent of the companys boatbuilding production.
Com-Pac operates as a combination manufacturing and assembly plant, since hulls for the larger boats are laminated off-site by JMJ Fiberglass, which specializes in fiberglass and has had a 15-year relationship with Com-Pac.
Were not interested in being in the glass business, because its a specialized business and requires a huge commitment for space, Rich Hutchins explained. However, we dictate lamination schedules, and store and maintain the molds between production runs. (We found fiberglass and gelcoat surfaces on our test boat to be smooth, with no evidence of print-through or crazing.)
The Com-Pac manufacturing facility comprises three buildings housing assembly areas, and metal and wood shops. Dealers are located in most major sailing ports. The company has delivered boats to the Great Lakes and all three U.S. coasts. Many 35s are currently cruising the waters of the Caribbean and the Florida Keys.
The target market for the 35-footer is the experienced sailor stepping up from a smaller boat who wants to sail offshore.
Design
Designed by Charley Morgan, the 35 was introduced 24 years ago as a 33-footer with a standard transom. However, when the market demanded the addition of a swim platform, the molds were retooled, and the stern swept aft, adding one foot to the waterline.
She is a traditional, beamy cruiser, Rich Hutchins explained, typical of Charleys designs.
Morgan divided the design criteria into four elements: She had to have a shoal draft, be stable and sea kindly, and fast enough to give good results under PHRF rules. To that end, Morgan combined a large sailplan with moderate displacement, a long waterline, generous beam, and a Scheel keel.
The patented (Henry) Scheel keel design is wider at the bottom of the keel than in the middle section. It widens again at the top where it joins the hull, so that the cross-section resembles an elongated chemistry flask. The width is achieved through a gentle, concave curve. As with a wing keel, or bulb keel, the broad section at the bottom creates a large area to place ballast down low. The bottom is curved to reduce drag at the base of the keel.
Proponents claim a Scheel keel will work better to windward than other shoal-draft designs, but once you start reducing the leading edge of a keel, the gains in performance are slight. In our opinion, the wing versus Scheel keel debate should be more focused on practicality, and at least, the Scheel keel is less likely to foul a rode or snag a reef than some wing designs.
Rich Hutchins described the shoal-draft Scheel keel as the perfect keel for a cruising boat, compared to a full keel. The design incorporates a wide trunk that runs to a significantly wider foot filled with lead ingots. The design provides excellent lift, allows the boat to turn in her length, and to access shallow anchorages.
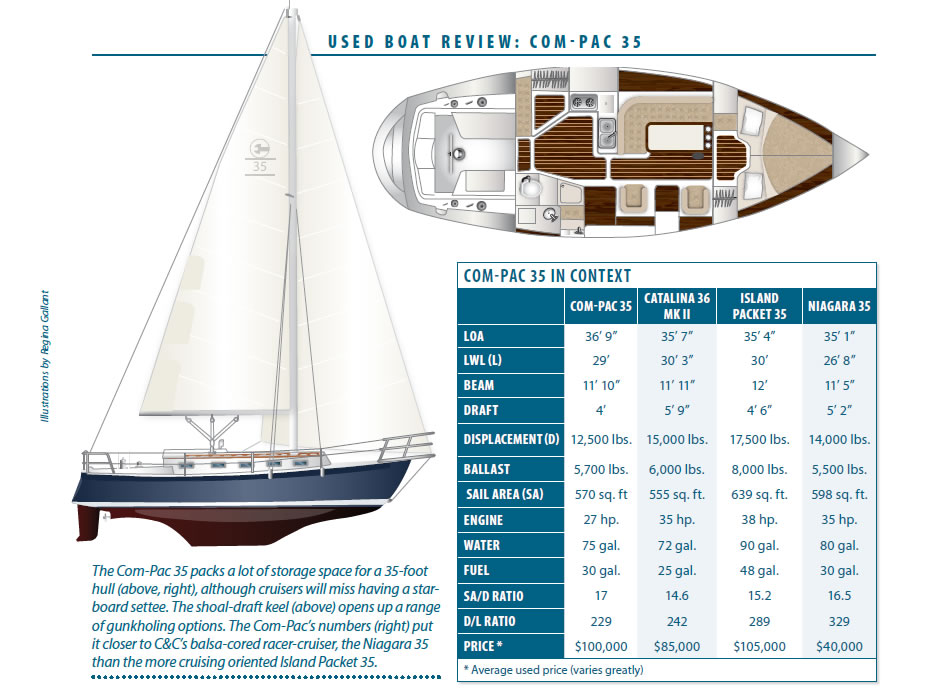
The Com-Pac 35 displaces 12,500 pounds, of which 5,700 pounds is ballast. The sail area to displacement ratio is 17.2, typical of this breed of boat, and the displacement to length ratio is 232.5-a moderately light ratio. We expect it to outperform many similarly sized performance cruisers, although the shoal draft does limit its windward performance compared to deeper keel boats.
The Com-Pac 35s profile reflects Morgans keen eye for aesthetics. The boat has slightly sloping sheerline accented by a bowsprit that lends a traditional look while increasing the sailplan. The sprit also facilitates the use of large light-air sails, eliminating the need for a spinnaker pole and associated gear.
The rather high-profile cabintop, which is 18 inches tall, creates headroom below while providing light and ventilation through five ports.
A teak eyebrow, and two teak handrails running the length of the cabintop add just enough brightwork to give the appearance of a cruising boat, without making it high maintenance.

Photo by David Leo
Deck Layout
Sailhandling arrangements feature internal halyards, a mast free of winches, and sail controls led aft to rope clutches. The single-spreader spar is made by Charleston Spars, and standing rigging is wire.
Halyards are led through Harken turning blocks installed at the base of the mast to Spinlock XT rope clutches. The main traveler sits on a heavy stainless-steel bracket attached to a 6-inch-tall molded fiberglass pod at the front of the companionway. The traveler, which is 14 inches above the cabintop, avoids chafing the gelcoat.
Coachroof winches are Harken two-speed 32s, while primary winches are Harken two-speed 40s. The headsail-trimming tracks are located on the rail. They are 68 inches long, enough to produce proper sheet-lead options for an oversized genoa or a blade.
Deck hardware standard equipment includes a Hood furler, though our test boat was equipped with an optional Profurl. Not our favorite furler (see PS August 2009 online), Profurl models have held up well over the years, so long as the high-carbon steel bearings are monitored for corrosion.
The 34-inch-long bowsprit supports a beefy stainless-steel plate 24 inches long and 12 inches wide, fitted with double anchor rollers. It appears to be sturdy enough to support the loads of two anchors.
Theres room between the stem and the forward end of the cabin trunk for a dinghy on deck, or for stretching out.
Stanchions are only 25 inches high, too short for our taste, especially since the toerail is only an inch tall. The decks on our test boat were covered with a heavy dew, so we appreciated the very aggressive nonskid on the deck, cabintop, seats, and coaming.
The boat is well-ventilated. Two 20-inch by 14-inch hatches are located on the bow, and pairs are mounted under the boom and at the aft end of the cabintop. Add a companionway measuring 38 inches long when open and dorade boxes near the front of the companionway, and fresh air moves easily into all spaces belowdecks. This is a boat naturally equipped to deal with the heat of a Florida summer.
The T-shaped cockpit is well laid out and comfortable. It measures 44 inches from wheel to companionway and 25 inches between seats. The well is 15 inches deep. Seats are only 50 inches long, adequate for seating two adults but too short for stretching out for a nap.
Stereo speakers are built into a recessed cubby in the coaming where they are safely out of the way; a second cubby with fiddles provides storage for winch handles and sunscreen.
The helmsman is elevated by a slightly arched seat aft of a 36-inch destroyer-style stainless wheel. Theres good visibility over the top of the wheel. Like many builders, Com-Pac installs oval-shaped teak seats on the stern corners, offering a comfortable perch for daysailing.
Standard equipment in the galley is an alcohol stove, which Rich Hutchins said meets the needs of most owners and satisfies those with a concern about the volatility of propane (LPG). While many owners are content with the wick-style alcohol stoves (particularly those who seldom bake), the advantages of LPG became clear in our review of marine stoves (see PS July 2007 online). LPG remains our preferred means of cooking onboard for longer-term cruising, so long as the owner is serious about properly storing and using LPG onboard (see PS March 2014).
Aboard the Com-Pac 35, the optional propane tank is located in the open area beneath the helmsmans seat. Any leaked gas can drain into a scupper below the seat. Compared to other dedicated propane lockers, this is more exposed. Wed like to see more protection for the tank and gauge.
The starboard lazarette is cavernous. It provides storage for sails or an inflatable dinghy, and access to the steering unit and through-hulls. A 30-gallon aluminum fuel tank is located aft of the engine, leaving space for a heater or generator.
One owner reported that he had to replace his fuel tank, due to pin-holes in the bottom caused by poultice corrosion. On his boat, the tank rested on a plywood base that absorbed moisture-a construction no-no. The new tank was placed on a non-hydrodscopic Starboard, preventing potential future poultice corrosion problems.
A three-cylinder Westerbeke 27-horsepower diesel is standard on the Com-Pac 35. The engine fits very snugly in a soundproofed compartment, making it a challenge to work on, in our opinion. Rich Hutchins disagrees.
One Com-Pac 35 owner told us that checking the oil level is easy, but that changing the oil is more difficult and checking the water-pump impeller is a chore.
In order to create space in the aft cabin below, the port lazarette is only 8 inches deep. However, its 30 inches long and 17 inches wide, and provides good stowage for fenders, lines, and other oft-used items. This is actually a better arrangement than having to invert ones self, digging for something that has migrated to the deepest part of a voluminous locker.
Considering the extensive list of standard gear, our overall impression is that the boat is well-equipped. The boat owner interested in improving performance will want add a vang, an inboard track for smaller headsails, an adjustable backstay, and perhaps spinnaker gear.
Accommodations
The Com-Pac 35 is spacious, well-arranged, and nicely finished belowdecks. Standing headroom is 6 feet, 4 inches. Access, however, is down a relatively steep ladder.
The head is to starboard at the foot of the companionway, and the nav station is forward. Also to starboard are two heavily upholstered swivel chairs surrounding an entertainment center. One chair swivels to provide a seat for the navigator, who sits opposite the L-shaped galley, which is located to port.
The entertainment center houses a cocktail table, TV/VCR combination, AM-FM radio, and CD player, all standard equipment. Two halogen reading lights to starboard and three to port provide excellent lighting. Sleeping cabins are to port in the stern and in the bow.
The centerpiece of the main saloon is an L-shaped settee and dining table hinged to the forward bulkhead. The table is large enough for four adults. When out of service, it swings up to enclose a large cabinet mounted on the bulkhead, significantly increasing the space available for storing plates and cutlery. The cabinet, 10 inches deep and 20 inches wide, with six compartments, is very well made-one of the best weve seen.
With the tabletop stowed, the space converts to a 6 foot by 8 foot conversation pit. The settee also folds out to make a wide, 72-inch-long berth.
The galley has some interesting wrinkles. A hinged board on the aft bulkhead drops to cover the stove, producing a 24-inch by 42-inch countertop adjacent to the reefer/dry locker. Double stainless sinks are standard, as is a microwave. Another unique feature is a hinged shelf at the inboard end of the counter that rotates downward to provide a drink tray for the galley slave.
Storage for pots and pans is below the stove, which, on our test boat, was a two-burner LPG Hillerange stove-oven combination, a $1,360 option.
The head has a shower with a seat separated from the main area by a half-height plexiglass partition. Adding a curtain would help keep spray out of the main compartment. There is a great deal of potential storage space in the fiberglass panliner beneath the seat. Some owners have used deck-plates or small plastic access hatches to create more storage there.
The port stateroom aft is rather spartan, consisting of a double berth and hanging locker; its ventilated by hatches overhead and in the cockpit. Clearance between the top of the berth and the bottom of the cockpit is a meager 21 inches.
The forward stateroom is enclosed by a door with an arched top, a nice touch. Furnishings include a small seat to starboard, a hanging locker large enough for four sets of foulies, and storage shelves running the length of the compartment. The berth measures 84 inches wide at the head and 76 inches on centerline.
On balance, we think Morgan did an excellent job of apportioning space, since two-thirds of the boats living spaces are in the cockpit and saloon. The cockpit seats six comfortably; space for four, possibly six diners is adequate, and sleeping quarters are large enough for an extended cruise.
The swivel chairs and L-shaped settees are a poor choice for offshore passagemaking; theyre better suited for sailing from port to port alongshore.
Performance
With assistance from Max Heller of SeaCraft Yachts in Seattle, we tested the boat on Lake Union on relatively flat water. It motored easily and quietly at 5 knots; company literature indicates that itll do 8 knots under power at top speed with the standard Westerbeke. While leaving the dock with a light breeze on the beam, the boat easily backed up in straight line. A three-blade propeller stops it quickly, and the boat spins 360 degrees in one boat-length.
We sailed under full main and a 135-percent genoa on the furler. In 6 to 8 knots of wind, it sailed easily at 5 to 5.5 knots,; it buried a shoulder and squirted forward in the occasional puff. The boat was surprisingly nimble considering its design and displacement; it sails well to weather and tacks quickly. The Scheel keel produced a stiff ride-a surprise on a shallow-draft cruising boat.
One owner told us he cannot beat inside 100 degrees, but we matched that number easily, and think a properly tuned rig and well-cut sails will produce 90- to 95-degree tacking angles consistent with a sloop. It cannot, however, be expected to perform on par with a competitive fin-keel boat. PHRF numbers in various fleets range from 147 to 167.
Since we saw 5-plus knots of boatspeed in light air, we suspect performance in moderate winds will be solid. Morgan described a downwind sail under spinnaker in heavy seas on the Gulf of Mexico during which the boat recorded bursts of 11-knot speed. Thats well outside the average curve for a 35-foot, moderate-displacement cruiser.
Conclusions
The boats speed and maneuverability in light air was impressive. In this case, the Scheel keel provides shoal draft with minimal cost to performance. The boat points well and goes as fast as other boats that we might call moderate-performance cruisers.
The deck layout is typical of its contemporaries, and its easy to move about the deck to handle sails. Accommodations belowdecks are spacious and reflect the builders attention to detail. The Com-Pac 35 is outfitted with an extensive list of standard gear that includes sails and furler, deck gear, well-equipped galley, television/stereo/CD players and speakers. Add a downwind sail, electronics package, and autopilot, and its ready for extended cruising.
The boat, which listed for about $150,000 in 2001, has held its value relatively well. The limited production run keeps it under the radar of most boat searches, which has neither hurt nor helped prices. In some respects, it is a niche boat, holding particularly strong appeal to a couple who wants to sneak into shallower areas of the Bahamas or slip in and out of the Intracoastal Waterway without fear of running aground, or resorting to a centerboard.
Morgans long years on the west coast of Florida and familiarity in the Bahamas showed him early on that some of the best nooks and crannies are off limits to a boat that draws more than 5 feet. Com-Pac has done a good job keeping the boat practical to sail, nice to look at, and not a chore to maintain.