Beneteau has been building sailboats for 120 years, but it’s unlikely that patriarch Benjamin Beneteau ever envisioned his boatyard becoming a vertically integrated company with more than 4,500 employees. Nor could he have imagined that three-dimensional, computer-aided design would drive a five-axis robotic shaper that could turn design ideas into tangible hull shapes sans shipwrights. However, he did see the staying power of sailing and knew it would stand the test of time. Beneteau’s sheer size affords an opportunity for significant research and development, and designers get to interface directly with the production team throughout the boatbuilding process. There’s also a scale of economy factor that’s best demonstrated by the 300-person crew working at Beneteau’s expansive woodshop in Vendee, France. The facility fabricates and finishes interiors for Beneteaus built all over the world.

Today, the multinational company relies on an in-house design team, plus a stable of top yacht designers who remain on call. The result is that Beneteau has become a trendsetter even in tough economic times, and part of this success lies in its differentiated two-tier (race and cruise) approach to boatbuilding. By offering different boats to racers and cruisers, the world’s largest production boatbuilder more effectively caters to the needs of each market. This has served the company well for decades. For example, the Oceanis line of cruisers was birthed in the 1980s, and the current series offers a whole new array of design attributes.

DESIGN
The Oceanis 41 features a new hull shape and a new cruising perspective—a design that focuses on style, comfort, and ease of operation. It’s clearly an effort to make mid-size cruising boats more user-friendly than ever before, and to achieve that end in distinctly European styling.

Beneteau’s marketing literature for the Oceanis 41 boasts eye-catching, flat-water, point-to-point sailing and a luxury cruising lifestyle. Missing are photos of the guys with wornout sweatshirts and week-old beards slogging into a cold gray sea. Cabin photos brim with countertop knick-knacks and long-stem wine glasses that would scatter like pins in a bowling alley when the first gust hit. However, after sailing the boat ourselves and getting a feel for this brand new, wide-body sloop, Practical Sailor testers walked away far more impressed by the boat than by its marketers’ depiction.
Designer Finot-Conq skillfully distributed the new boat’s volume, placed the rig and foils exactly where they hydro-dynamically belonged, and revised the deck layout. Looking at the waterline footprint, topside flair, and profile of the Oceanis 41 reveals some of the not-so-subtle changes in canoe-body design. For instance, a chine-like edge interrupts the smooth curve of the topsides. Affectionately known as the “kink,” it appears throughout the Oceanis line, and its fore and aft run acts as a water release when the boat is heeled and beating to weather. It’s certainly an aesthetic change to the smooth compound curves and flares seen in the topsides of earlier Beneteaus, and its performance-enhancing potential will be a topic of conversation for some time.
Another notable design change is the sailboat’s wedge-like shape and the distinct trend in carrying near max beam all the way aft to the transom. This feature almost begs for a twin rudder approach to steering. Interestingly, rather than adding a second rudder, Beneteau used a deep, semi-balanced spade rudder. It effectively resists cavitation and the inevitable broach, until you are so overpowered that you deserve the big surprise that comes with a spin out. Even then, the Oceanis is well behaved as it politely rotates into the wind without a neck snapping auto tack.
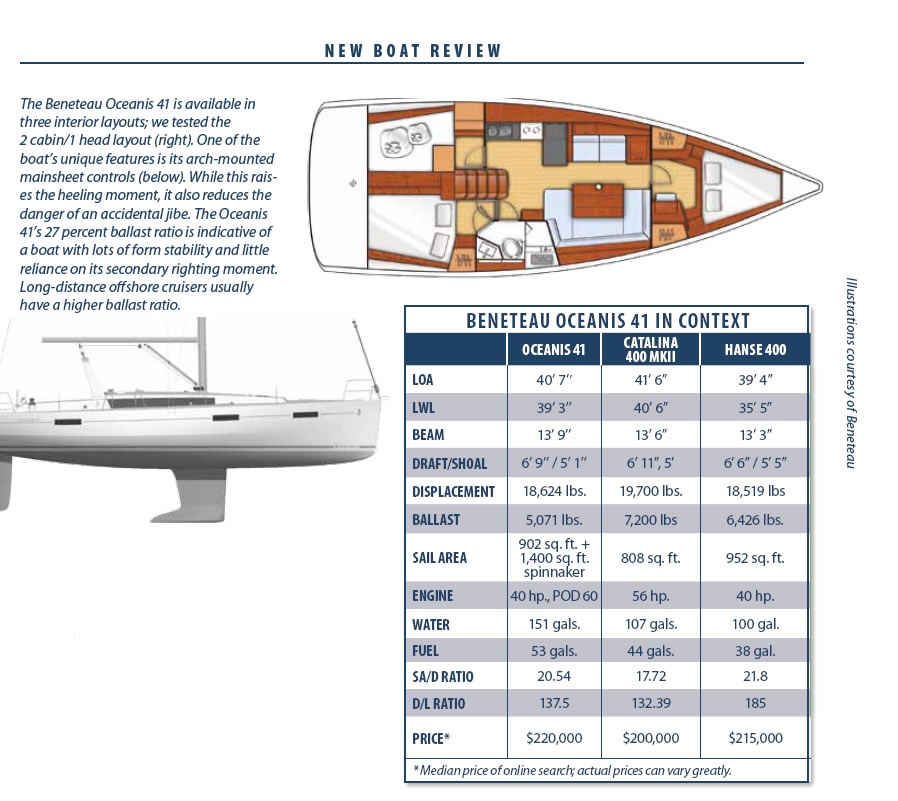
The Oceanis’ kink and wide beam carried aft are traits that first arose in modern race boats, and it’s a trend that adds form stability, increasing the amount of sail-carrying capacity. It also adds space both below and above deck. The new 41 comes in deep (6 feet, 9 inches) and shallow (5 feet, 1 inch) draft versions, and those planning on longer-range offshore sailing, or those who simply prefer better windward ability in a cruising boat, are much better off with the deep-draft alternative.

Beneteau has a penchant for detailed engineering, and the new Oceanis line has gone through quite a bit of R&D. The company also shows an inclination for retaining what works and evolving good ideas. Like its siblings, the Oceanis 41 shows a lot of this tried and proven lineage, especially in construction scan’tlings, but it also has taken some bold new strides. For example, the recent advent of the pod-type, rotating sail drive links up with the bow thruster to create what Beneteau calls the “Dock and Go” system. This optional, joystick-actuated feature makes maneuvering in tight confines a piece of cake, but it also adds more system complexity and cost to the boat. And although the system makes docking a dream, we’re not sure what future maintenance issues and costs would add up to. A 41-footer with a conventional sail-drive and no bow thruster might save a buyer a few thousand dollars, but it would also put more of the close-quarters handling challenge back in the hands of the crew.

DECK DETAILS
From stem to stern, there’s a lot of innovation, and many of the new trends are found aft of the companionway. The first is a twin-wheel helm, a sensible response to the wide beam carried so far aft. It offers the helmsperson a comfortable windward or leeward perch. The resulting wide centerline alleyway would have been an awkward traverse underway if it weren’t for the convenient cockpit table that doubles as a good handhold, a bracket for a chartplotter multifunction display, and even a convenient fiddled catch-all, complete with drink holders. At anchor, the narrow, well-secured centerline table spreads its gull-wing leaves and turns the cockpit into a great place for dinner or a handy gathering spot for impromptu gams.

Another interesting feature is the transom: A pushbutton transforms the aft deck/helm seat into an open transom with a swim platform. The electric open/close servo causes the hinged transom to rotate from the vertical to a horizontal position, morphing what was a stern enclosure into a swim deck replete with a stainless-steel boarding ladder. The result is a wide spacious aft portion of the cockpit that’s convenient for swimmers, snorkelers, and families who love to play in the water. The transformation is fast, so if a building breeze causes the anchorage to become less bucolic, the stern appendage can be quickly reeled in, turning the transom back into a safe enclosure.
Another feature in the cockpit makeover is the elevated mainsheet traveler that sits on a well-reinforced fiberglass (FRP) arch. With the traveler and sheet out of the way, there’s room for a dodger/bimini and less risk of someone being whacked by the mainsheet tackle during a jibe. The setup does mean that the boom is higher off the deck, and the heeling moment increases a little for the same amount of sail area, but on a cruising boat, these seem to be fair tradeoffs. Sail shaping, trim, and outhaul-inhaul lines, along with reefing lines, are clustered around rope clutches on either side of the companionway.
On deck, there’s a practical form-meets-function theme to many of the styling changes. A lot of attention has been given to providing a very usable set of anchor rollers. The nicely executed custom stainless-steel assembly projects far enough forward to keep anchors from chewing up the gelcoat during deployment and retrieval. The solidly fastened anchor roller projection can also double as the tack point for a light-air, removable furling jib or asymmetric spinnaker. The structure includes a tension/compression strut that spreads loads to a secondary point further down the plumb stem. The roller assembly is another good example of practical and aesthetic utilitarian engineering.
This theme is carried aft with a teak-like PVC toerail that affords a hint of woodwork, hides the hull-to-deck seam, and provides an effective foot stop when the boat heels before a gust. At the stem and stern, as well as amidships, lie breaks in the toerail where well-fastened cleats are mounted. By giving primary billing to cleats that are ready to fair-lead lines in a wide arc, Beneteau shows its roots as a seafaring company. It doesn’t try to hide essential hardware, instead recognizing its importance and blending it into a functional design approach.
Testers also were pleased to see a well thought-out anchor well and a usable—albeit small—windlass. A snubber line can be fair-led from a bow cleat to an all-chain anchor rode and the load transferred from the windlass gypsy. There’s even enough room for a second anchor’s rope rode. Whether it’s a well-placed spring-line cleat or a functional set of anchor rollers, cruisers will come to appreciate their value in tough anchoring conditions or challenging docking situations. The same goes for the value of the rugged forestay chainplate on the Oceanis 41 foredeck. Those heading offshore need more than a roller-furling genoa and a mainsail to cope with the wide range of conditions they will face. An optional removable forestay and hank-on, heavy-weather jib or storm jib are available to add the needed sailplan versatility.
One of the more subtle and most beneficial redesign elements aboard the 41 is the rig. The mast has been moved aft to about 47 percent of the distance from the bow to stern. This adds more J to the fore triangle and allows a barely overlapping jib to be set on a 15/16th headstay. It’s a win-win for the owner and the builder as it enables shrouds to be run to an outboard chainplate, maintaining inboard sheeting for the headsail. This also allows for easy passage when walking the sidedecks. The builder avoids both the extra cost and headache of inboard chainplate reinforcement, and the higher loads resulting from narrow athwartship shroud spacing. The big tradeoff however, is not being able to point as high in light air when using a large overlapping genoa. Beneteau believes this isn’t much of a compromise as most are more likely to use a gennaker.
ACCOMMODATIONS
A built-in, five-step companionway ladder leads to the accommodations below. The wide steps with bolstered sides keep feet from sliding off when the boat is heeled. The entire ladder assembly can be pivoted toward the overhead, affording access to the forward part of the engine.

The Oceanis 41 offers a high-volume interior that’s available in three different layouts. We test-sailed the two cabin, one head version, but there is also a three cabin, one head format and a three cabin, two head option. The more cabins and heads, the less space for cockpit or pantry storage. The two cabin, one head layout had a roomy feel, but it did not have functional port and starboard sea berths. A sliding nav station/end table occupies the port portion of the main saloon and allows the settee and nav table to be reconfigured into two seats with a small table in between. Those making offshore passages will regret not having a usable berth in this part of the boat, and the lack of a traditional chart table/nav station will be a notable con for some sailors.
There’s a functional, L-shaped galley with a two-burner stove, small oven, and a top-loading fridge, but counter space is limited.
The accommodations in all three configurations feature private cabin berthing situated at opposite ends of the boat. Though ideal while moored or when anchored in cooler climates, boat motion and the lack of ventilation underway will make such berthing less appropriate for passagemakers. (There are no full-sized Dorade boxes, only a hatch mushroom vent and a small aft-facing scoop.) However, Beneteau certainly knows it market, and the apparent trend seems to be toward fewer hours of sailing, and increased time spent entertaining and weekend cruising—dynamics that have certainly driven the new boat’s interior design.
CONSTRUCTION
Those with a wooden-boat school awareness of joiner work will be a little disappointed by today’s approach to production-boat interiors, and Beneteau is by no means the only builder that features raw-edge plywood locker lids and cutouts along with non cut-to-contour interiors. The fact that it’s not the same level of craftsmanship as seen aboard custom yachts is not a deal breaker. There’s no need to tab in the joinery, because it’s not part of the structural framework of the boat. Many labor hours are saved with this prefab and nicely finished approach to creating interior woodwork.
Beneteau, like many others, has opted to provide value to customers by not building interiors in situ, and investing the labor savings in better-engineered laminates and other crucial aspects of production building. In essence, to keep the price more competitive, the hours spent on detailed joiner work have been cut and the styling approach favors the factory-built interior. In some ways, this is good for Beneteau and the buyer: It allows for a greater percentage of the building budget to be allocated toward laminating materials, rigging, mechanical, and electrical systems—where many feel it really belongs. And it doesn’t mean that the interior finish quality has been abandoned; it simply means that if you are looking for dovetailed drawers, a solid teak-and-holly sole, and other nostalgic tidbits of yachting’s gilded days, you need to look elsewhere and be ready to double or triple your boat-buying budget.
PERFORMANCE
We tested a deep-draft Oceanis 41 in 17- to 20-knot conditions (with a few higher gusts) and found the boat to be responsive under sail and willing to tolerate the gusts. Intentionally, we drove the boat hard on the wind, assuming that such a wide stern would turn a deep heel into a rudder-releasing roundup. Not only did the boat refuse to round up, but it maintained a comfortable helm despite a 20-plus degree heel. Only when puffs bore down at a sustained 25 knots did the rudder finally lose its grip. The result was a very demure return to an upright trim as the boat came head-to-wind. This was a far cry from the ricochet roundups we’ve experienced on other cruising and racing boats with wide sterns.
The boat we tested was rigged with the optional mainsail furling system. Reefing the batten-less main with the furler was easy, as was reducing headsail area with the roller furler. With less sail area set, boat handling was smooth and decisive; heel lessened to 15 degrees, and the boatspeed still exceeded 7 knots on a close reach. We were riding with the lee side just about level with the kink, and the water seemed to resist wrapping up around the hull. It was also interesting to see that the transom wasn’t immersed and the quarter wave seemed minimal. All of these attributes are indicative of Beneteau’s design success with the new hull form.
Off the wind, we unwound the reefed working sail area and scooted along at about 7.5 knots. A furling gennaker or asymmetric spinnaker could be tacked to the end of the anchor rollers and would have added even more boat speed, but in the 20 knots of true wind, there was no need for the extra drama.
With the sails dropped, the Yanmar 40 horsepower engine had plenty of power to handle the conditions. Returning to the dock and backing into a tight slip would have been a chore without the Dock and Go joystick steering—a benefit of a rotatable saildrive and bow thruster electronically linked to a thumb and forefinger actuator.
CONCLUSION
We liked the fact that the new Oceanis 41 carries on Beneteau’s tradition of keeping enough FRP structural material in the boat to maintain its reputation for well-built hulls. This boat is no featherweight, and with an 18,000-pound-plus light-trim displacement, it’s a sizable 41-footer. Light air may need to be handled under power, but the crew also has the option to harness a 1,400-square-foot asymmetric spinnaker.
The Oceanis 41 comes standard with a conventional main and a lazy jack sail pack. Those who want peak light-air performance should opt for this setup, but those seeking operational convenience may want mainsail furling—because the arch raises the boom fairly high, the air draft is 64 feet, quite a halyard haul.
Those headed on a lengthy offshore passage will bemoan the lack of functional seaberths, and they may want to think about the six large portlights and the damage control that would be required should one crack or let go.
All in all though, the Oceanis 41 is a modern hull form with a stylish interior that best fits the needs of part-time cruisers looking for a lot of boat that’s a lot of fun under sail.
This article first appeared on January 09, 2012 and has been updated.



































How does this review of a fat stern video square with the video condemning them all to terrible upwind performance?
You mention large hull portlights as a con. Why?